Fig. 4.
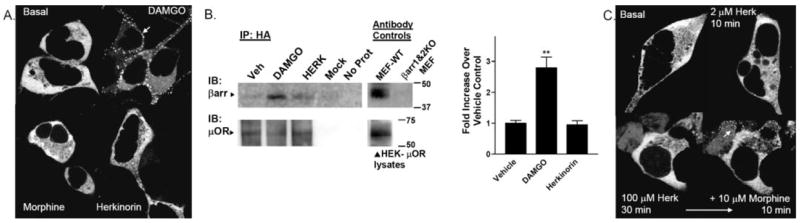
Agonist-induced β-arrestin interactions with μOR in HEK-293 cells. HEK-293 cells transiently transfected with μOR and βarr2-GFP were imaged in real time after agonist treatment at room temperature. The cytosolic distribution of βarr2-GFP is shown in the untreated cells in the top left. A, βarr2-GFP translocation to μOR in HEK-293 cells. DAMGO (1 μM) treatment leads to βarr2-GFP translocation within 5 min (white arrow, punctate accumulation at membrane) whereas morphine (10 μM, 10 min) does not. Herkinorin (2 μM, 10 min) does not induce βarr2-GFP translocation. B, coimmunoprecipitation of β-arrestins and μOR after drug treatment. Cells were treated with vehicle (0.1% DMSO), 1 μM DAMGO, or 10 μM herkinorin for 5 min. Cells were then cross-linked using a cell-permeable cross-linking reagent (DSP). Cell lysates were immunoprecipitated by anti-HA-conjugated agarose beads, and proteins were resolved by SDS-PAGE under denaturing conditions. Blots (left), immunoblotting was performed using the β-arrestin antibody (A1CT); blots were stripped and then reprobed with the μOR antibody (Neuromics). Representative blots are shown. Mock refers to HEK cells transfected with empty vector. “No protein” contained no cell lysate in the immunoprecipitation. Antibody controls were performed on lysates run on the same gel as those shown for the immunoprecipitation. Densitometry (right), densitometry was measured from a total of three to four samples of each treatment prepared on 2 separate days. Shown are the means ± S.E.M. **, p < 0.01 versus WT or herkinorin (Herk), Student’s t test. C, βarr2-GFP translocation to μOR in HEK-293 cells overexpressing GRK2. Herkinorin does not promote βarr2-GFP translocation at 2 μM after 10 min or at 100 μM after 30 min. The same cells were treated with morphine (10 μM, 10 min) and βarr2-GFP translocates demonstrating that these cells do overexpress GRK2 because morphine does not induce visible translocation otherwise.
