Figure 4.
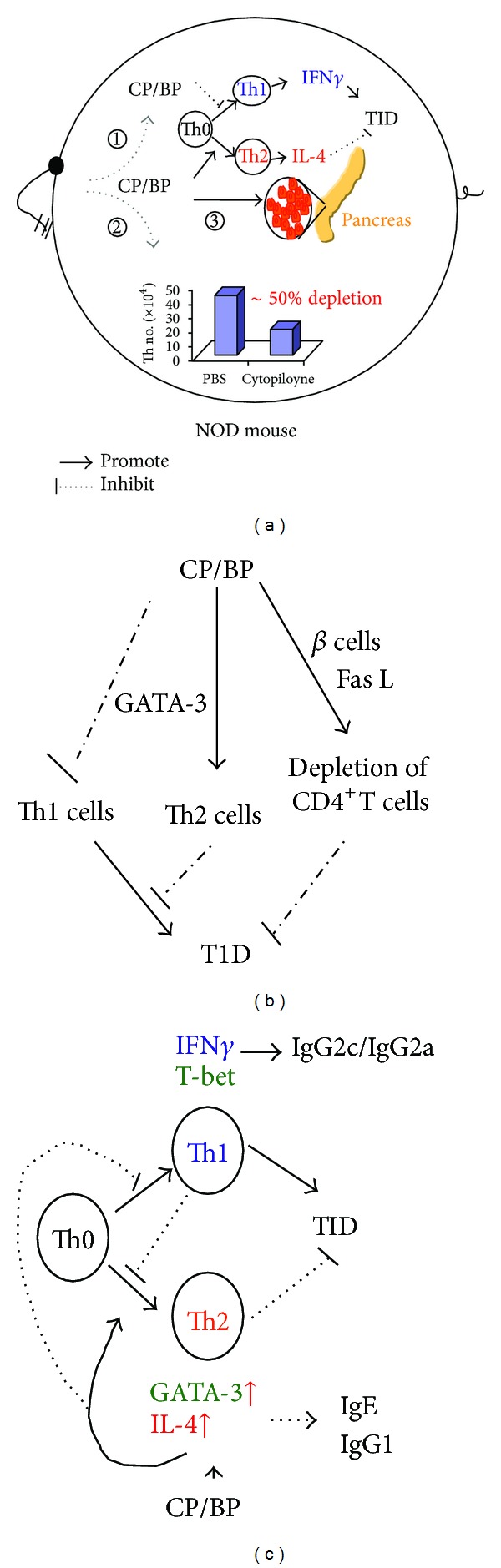
The underlying mechanism of the crude extract of B. pilosa (BP) and its active compound, compound 19 (CP), in T1D. BP and/or CP can suppress T1D development via regulation of T cells (① and ②) and β cells (③) in NOD mice (a). Their regulation of T cells involves Th cell activation and differentiation (①) and partial depletion of Th0 cells (②) as depicted (b). CP and/or BP augment the expression of GATA-3 gene and, in turn, promote the expression of IL-4 and Th2 cell differentiation. In contrast, CP and/or BP do not affect the expression of T-bet (c).
