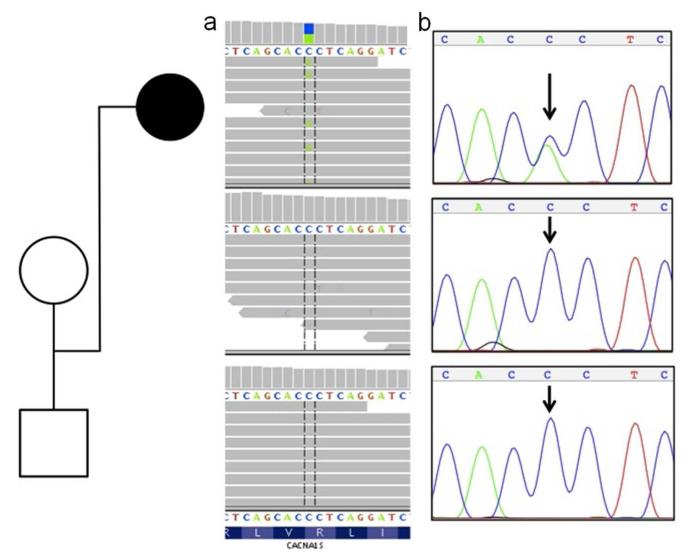
Figure 1.
De novo CACNA1S mutation in the affected trio. Whole-exome sequence reads (horizontal grey bars) (1a) show a C>A (blue/green block) change in approximately one-half of overlapping reads (vertical hashed lines) at the first position of an arginine codon (R) in the affected proband (top panel), and homozygous wild-type (C) reads for both unaffected parents at the same site (lower two panels). Sanger sequencing (1b) independently confirmed this as a de novo mutation in the proband.