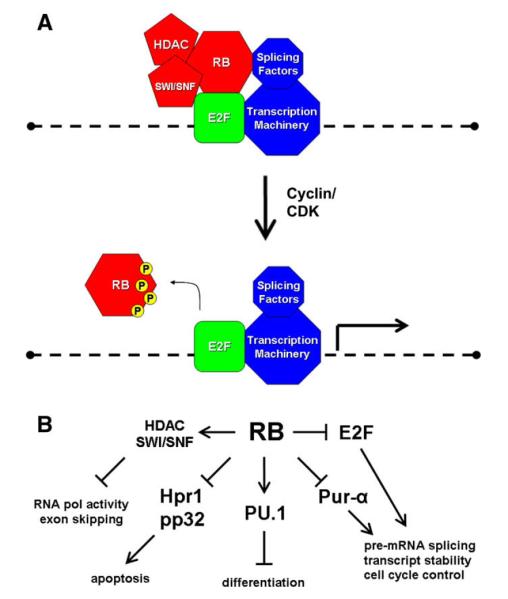
Fig. 2.
Models of RB/E2F and RNA processing control. (A) RB is bound to gene promoters through E2F. RB may inhibit splicing factors at promoters to suppress splicing of nacent RNA transcripts. Alternatively, RB may directly recruit splicing repressors. As the cell cycle proceeds toward S phase RB is phosphorylated and released from the promoter, which relieves splicing suppression and allows E2F to stimulate transcription. (B) RB interacts with several RNA processing factors that may serve to regulate diverse cellular processes. The role of RB in RNA processing control is a relatively unexplored area of research that may yield many insights into RB function.