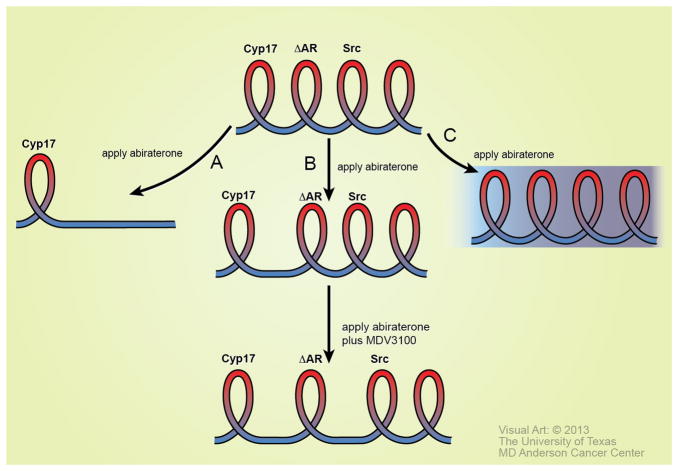
Figure 4. Possible outcomes of therapeutic treatments using the Spiral model.
A turn in the spiral is defined through the expression or alteration of a predictive marker. Three possible outcomes of therapeutic treatment may occur based on a predictive marker that defines a turn in the spiral. Abiraterone is used as an example. After application of abiraterone, (A) No further “turns” in the spiral occur, suggesting that the therapy may be curative. (B) The turn may be elongated, suggesting that abiraterone is effective in reducing androgen generated from Cyp17. Following the treatment, tumor adaptation may occur, leading to the next turn in the spiral. Successful application of the correct therapeutic agent at this stage of the spiral will elongate the next turn. (C) Application of targeted therapy does not have a positive therapeutic effect. This result would suggest that the tumor is in a more complex phase of the disease.