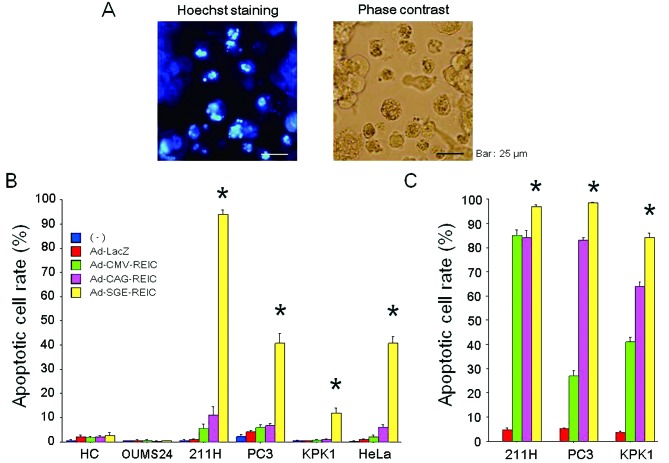
Figure 3.
(A) The induction of apoptosis after Ad-REIC treatment is shown by Hoechst 33342 staining in 211H human malignant mesothelioma cells. Apoptotic cells can be clearly observed as bright cells under fluorescence microscopy (left panel). The appearance of the cells by phase contrast microscopy is also shown (right panel). (B) The apoptotic cell rate (%) was examined after the indicated treatments (no treatment, Ad-LacZ, Ad-CMV-REIC, Ad-CAG-REIC and Ad-SGE-REIC at 50 MOI for 48 h) in normal human cells (HC, hepatocytes; OUMS24, fibroblasts) and various human cancer cell lines (211H, PC3, KPK1 and HeLa). The apoptotic cell rate was determined in five different fields under microscopic observations. *A significant difference was observed between the Ad-SGE-REIC group and the other treatment groups. (C) The apoptotic cell rate (%) was examined under different experimental conditions (Ad-LacZ, Ad-CMV-REIC, Ad-CAG-REIC or Ad-SGE-REIC at a 100 MOI for 72 h) in the human cancer cells (211H, PC3 and KPK1). *A significant difference was observed between the Ad-SGE-REIC group and the other treatment groups. SGE, super gene expression; REIC, reduced expression in immortalized cells; CMV, cytomegalovirus; MOI, multiplicity of infection.