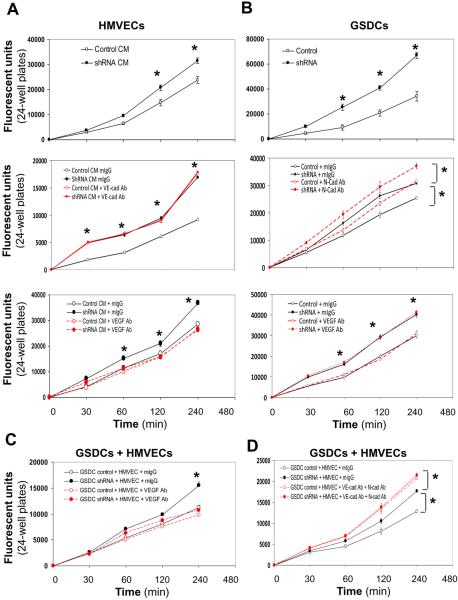
Figure 6. YKL-40 decreases permeability of HMVECs, GSDCs, and their combination in a manner dependent on VE-cad or N-cad activity.
A. HMVECs were plated on inserts and allowed to attach and spread. Cells were treated overnight with either GSDC control conditioned media (CM, 24 hr serum-free media) or YKL-40 shRNA CM (Top), control or YKL-40 shRNA CM with mouse IgG or an anti-VE-cad Ab (20 μg/ml) (Middle), or anti-VEGF Ab (100 ng/ml) (Bottom). Cell permeability was then measured using FITC-Dextran as described in the Methods. B. GSDC control or YKL-40 shRNA cells were used for the same permeability assay (Top) as described in (A), in the presence of an anti-N-cad Ab (50 μg/ml) (Middle) or VEGF Ab (100 ng/ml) (Bottom). C. GSDC control or YKL-40 shRNA cells were first plated on the insert. 2 hr following attaching and spreading, HMVECs were plated on the top of the GSDCs to form a second layer and allowed to attach and spread in the presence of mIgG or an anti-VEGF Ab (100 ng/ml). The same permeability assay was performed on the next day. D. GSDCs were pre-treated with mIgG or an anti-N-cad Ab (50 μg/ml) overnight to exclude the possibility that the top layer of HMVECs prevents the antibody from access to the bottom layer of GSDCs. Then, GSDCs and HMVECs were set up as described in C in the presence of mIgG or an anti-VE-cad Ab (20 μg/ml). The permeability was measured. N=6, *P≤0.05 compared to corresponding controls at the same time points.