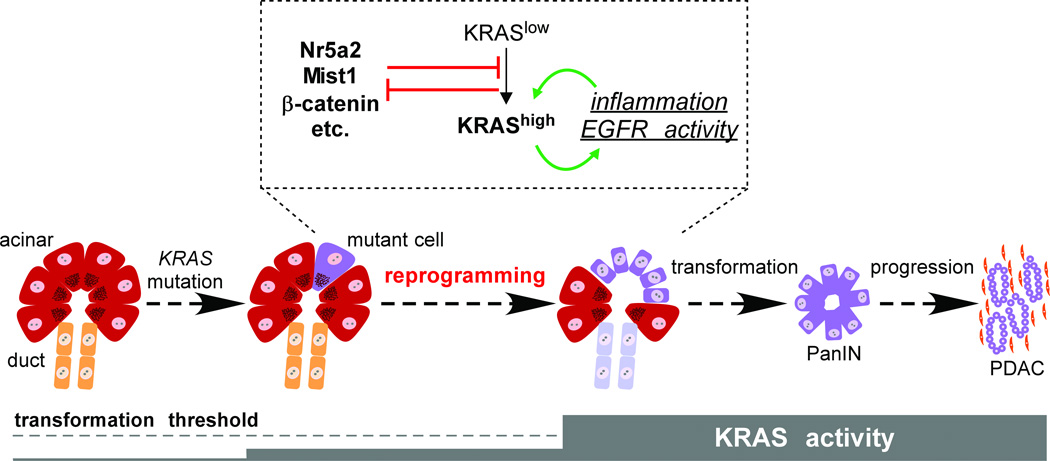
Figure 3. Acinar reprogramming in PDAC initiation.
PDAC originates from differentiated acinar cells, in which KRAS mutation alone does not elevate total RAS activity to the levels required for transformation. Acinar-ductal reprogramming occurs when KRAS signaling increases in response to exogenous inflammatory stimuli and/or EGFR agonists; as KRAS activity increases, mutant cells produce endogenous signals that establish a positive feedback loop between KRAS and inflammation. Several genes counteract acinar reprogramming, including Nr5a2, Mist1 and β-catenin, but are themselves inhibited by high levels of KRAS signaling. We hypothesize that acinar reprogramming represents a key step of PDAC initiation, which might be inhibited by anti-inflammatory agents in a chemopreventive setting.