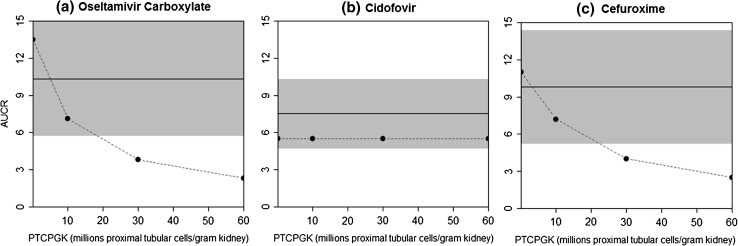
Fig. 2.
Evaluation of the effects of theoretical changes in the number of proximal tubular cells per gram kidney (PTCPGK) on plasma exposure changes (AUCR, severe renal impairment versus normal renal function) in severe renal impairment. The dashed lines represent the simulated AUCR, and the solid lines ± shade represent observed the mean ± SD AUCR. The tested PTCPGK values ranged from 0.1 to 60 million proximal tubular cells per gram of kidney. a Oseltamivir carboxylate: 100 mg oral multiple dose (single dose on day 1, twice daily on days 2–5, single dose on day 6) in subjects with severe renal impairment and healthy subjects [7]. b Cidofovir: 0.5 mg/kg intravenous infusion over 1 h in subjects with severe renal impairment and healthy subjects [9, 30] (note: in both simulated and observed studies, cidofovir was co-administered with oral probenecid to reduce nephrotoxicity). c Cefuroxime: 750 mg intravenous bolus dose over 2 min in subjects with severe renal impairment and healthy subjects [8]