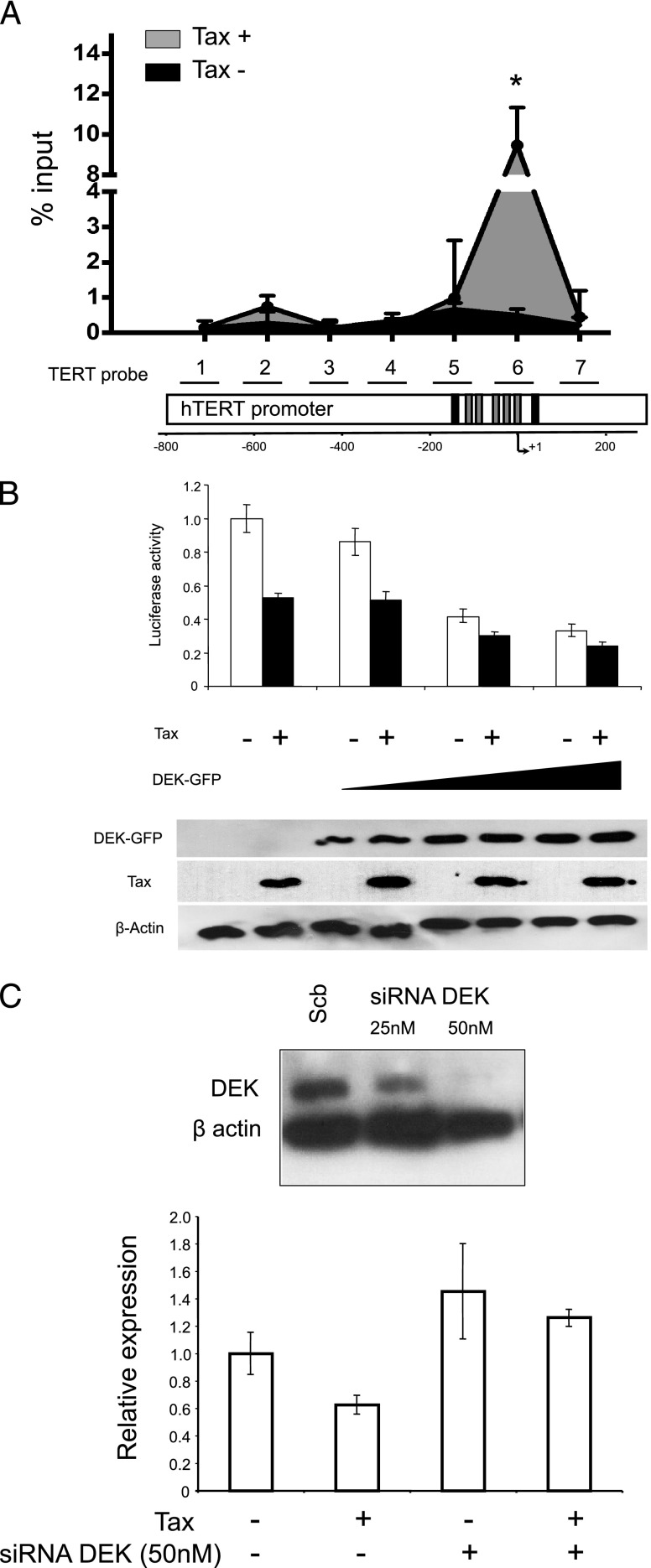
Figure 3.
DEK binds to and suppresses the hTERT promoter on Tax expression. (A) DEK and hTERT promoter association in Tax-expressing cells. The seven primer pairs used for ChIP and qChIP spanned a 964-bp region of the hTERT promoter. This region encompasses several known critical sites involved in the regulation of hTERT transcription, including the transcription initiation site, the start codon, as well as GC and E boxes. The black boxes represent the E boxes, while the gray boxes represent the five Sp1 binding sites. + 1 is the transcription initiation site. qChIP analysis of DEK association with the hTERT promoter was carried out as described in the Materials and Methods section. Results (means ± SDs) are representative of triplicate experiments. *P < .05, Mann-Whitney test. (B) HeLa cells were co-transfected with WT hTERT promoter-luciferase reporter plasmid TERTLuc800, in combination with the pCMV-Tax plasmid and/or a control vector (pCMV) in the absence or presence of increasing amounts of pNGLV3-DEK. Forty-eight hours after transfection, HeLa cells were collected and transcriptional activity was assayed by luciferase activity (see Materials and Methods section). (Bottom) DEK and Tax expression in transfected HeLa cells were assayed by Western blot analysis. (C) DEK knockdown increased endogenous hTERT expression and prevented its repression by Tax. hTERT expression was quantified through quantitative real-time PCR in HeLa cells transfected with the pCMV-Tax plasmid and/or control vector and/or the DEK siRNA (50 nM) and/or scrambled RNA. siRNAmediated knockdown of DEK expression was checked by Western blot analysis (top). Data shown in B and C are the means (±SDs) of one representative experiment performed in triplicate.