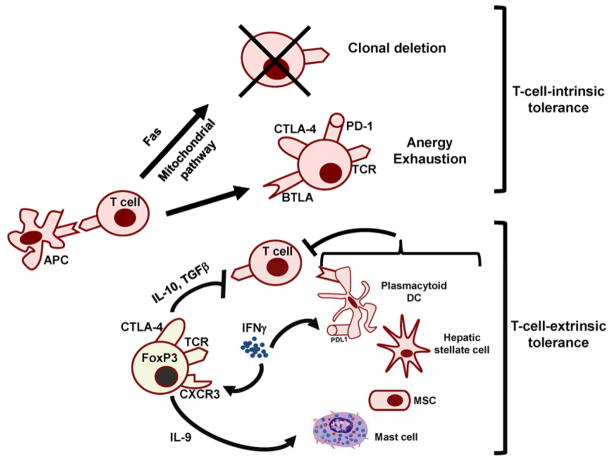
Fig. 3. Impact of infections on alloimmunity and tolerance mechanisms.
Infections result in the production of inflammatory cytokines, chemokines, and ligands for PRRs, resulting in signals that can enhance APC, T and B-cell activation, as well as antagonize adaptive cell-intrinsic and cell-extrinsic mechanisms of tolerance. Both result in augmented alloimmune responses within secondary lymphoid structures during priming as well as within the graft, ultimately leading to graft rejection.