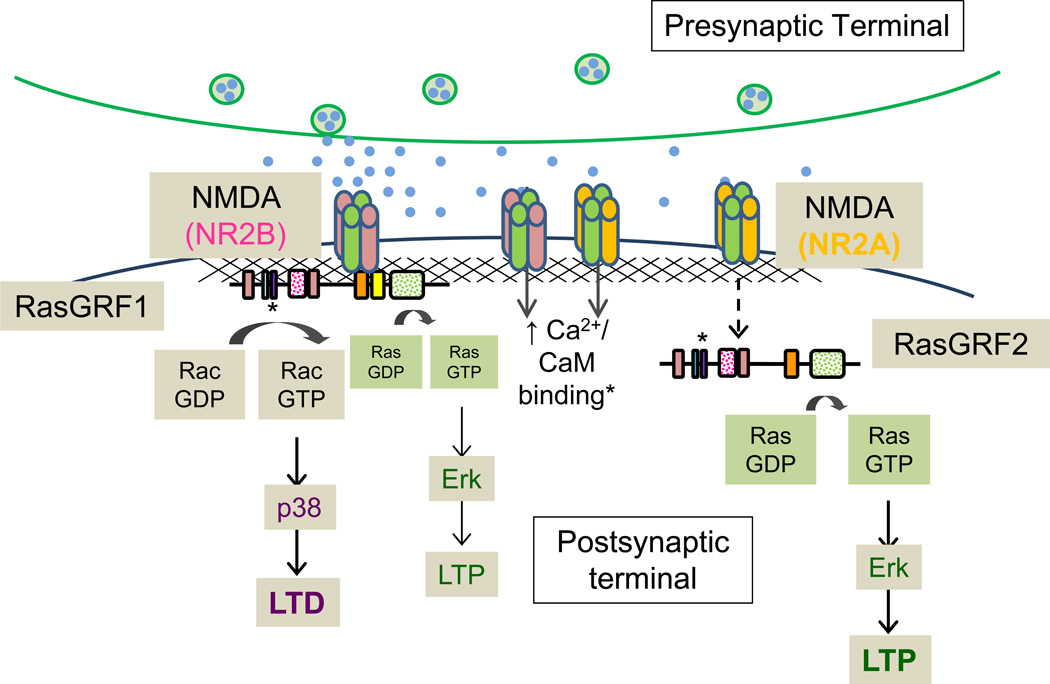
Figure 7. Distinct roles for RasGRF family members in NMDA-mediated long term plasticity.
Schematic illustrates proposed signaling mechanisms of the major RasGRF family members, RasGRF1 and RasGRF2. While both proteins are known to contribute to NMDA receptor-mediated Erk activity in vivo, data from biochemical and electrophysiological experiments suggest that RasGRF1 acts downstream of NR2B-containing NMDA receptors and signals predominantly through Rac and p38 to promote LTD in hippocampal slices. RasGRF2, however, signals almost exclusively through Ras and Erk following activation of NR2A-containing NMDA receptors to promote LTP.