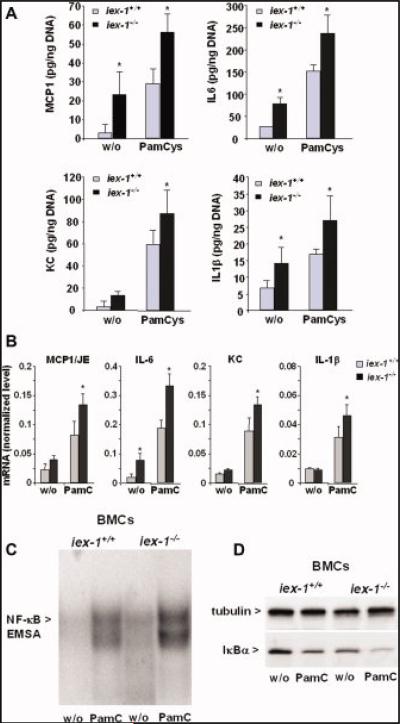
FIGURE 7.
Induction of proinflammatory chemo/cytokines and activation of NF-κB is greater in BMCs from gly96/iex-1–/– than in BMCs from gly96/iex-1+/+ mice. Supernatants (A) of BMCs from gly96/iex-1+/+ and gly96/iex-1–/– mice kept in culture for 72 hours and then subjected to Pam3Cys4 treatment (200 ng/mL) for 24 hours or not were submitted to ELISA detecting MCP-1, IL-6, KC, and IL-1β (data represent the mean ± SD of 4 independent experiments, *P < 0.05). Total RNA (B) of BMCs from gly96/iex-1+/+ and gly96/iex-1–/– mice kept in culture for 72 hours and then subjected to Pam3Cys4 treatment (200 ng/mL, 4 h) or not was submitted to reverse transcription and subsequent qPCR detecting MCP-1, IL-6, KC, and IL-1β or β-actin as control. The cyto- and chemokine mRNA levels were calculated after normalization to β-actin mRNA (data represent the mean ± SD of 4 independent experiments, *P < 0.05). Nuclear extracts (C) from untreated or Pam3Cys4 treated (200 ng/mL, 1 h) BMCs were submitted to gel shift assay for the detection of NF-κB; a representative experiment out of 3 is shown. (D) Cytoplasmic extracts from untreated or Pam3Cys4 treated (200 ng/mL, 30 min) BMCs were submitted to an anti-IκBα Western blot, and tubulin was detected as a Western blot loading control. A representative experiment out of 3 is shown. [Color figure can be viewed in the online issue, which is available at www.interscience.wiley.com.]