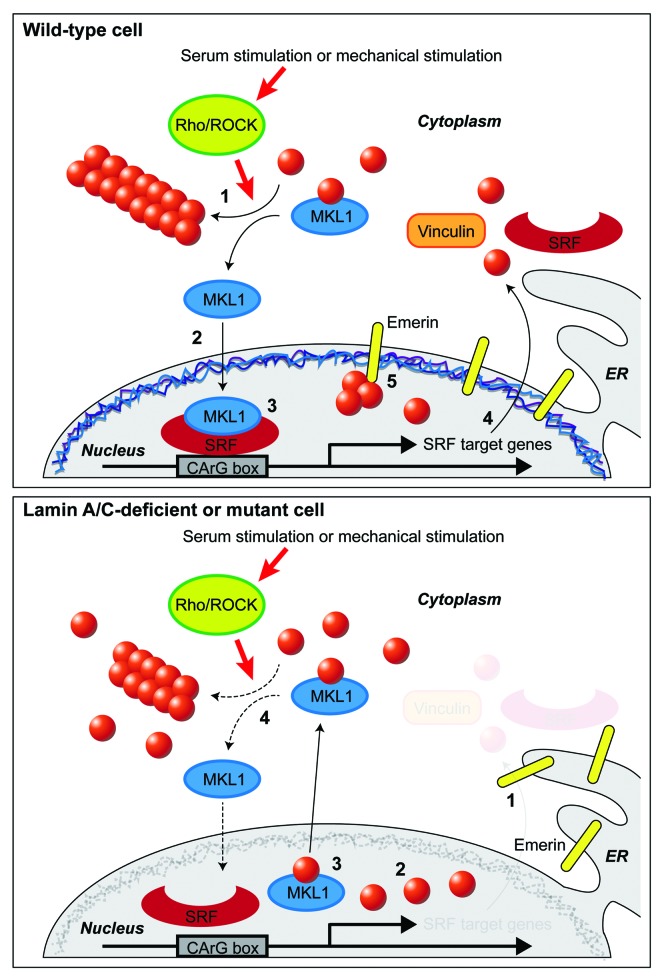
Figure 2. Schematic model of the interplay between nuclear envelope proteins and MKL1 signaling in wild-type and lamin A/C-deficient or mutant cells. Top: Sequence of events in a serum-stimulated wild-type cell. (1) Upon mechanical or serum stimulation, Rho/ROCK activity promotes cytoplasmic actin polymerization. (2) After being released from cytoplasmic G-actin, MKL1 translocates into the nucleus, and, together with SRF, binds to the CArG box to induce expression or MKL1/SRF-target genes, including actin, vinculin and SRF. (3) Emerin facilitates polymerization of (nuclear) actin. This reduces nuclear export of MKL1 which requires binding to nuclear monomeric actin. (4) Transcription of SRF downstream target genes occurs. Bottom: Sequence of events in a serum-stimulated lamin A/C-deficient cell. (1) Emerin is lost from the nuclear envelope and is unable to modulate nuclear actin polymerization. (2) G-actin binds to MKL1. (3) Export of MKL1 from the nucleus occurs. (4) SRF binding to its target element on the DNA and transcription of downstream target genes are impaired.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.