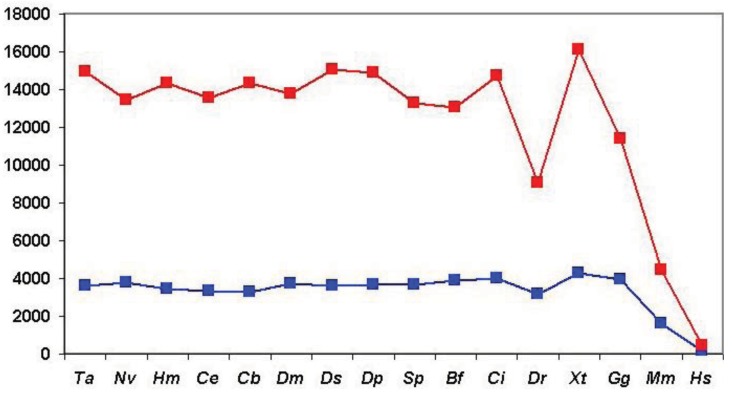
Figure 6.
Analysis of sequence similarity networks of paralogous human proteins defined through comparison of human Swiss-Prot entries with proteomes of Metazoanspecies. Clusters of homologous human Swiss-Prot entries were defined as sequences that gave the best match with the same entry in the given proteome using a cut-off value of e < 10−5. The species are listed in the order of decreasing evolutionary distance from Homo sapiens, thus the abscissa has a time-dimension but their distance is not drawn to scale. Blue rectangles represent the number of components (homologous clusters), red rectangles represent the number of human Swiss-Prot entries that are clustered by sequences of the target genome, i.e., that have at least one human paralog. Abbreviations on the abscissa: Ta - Trichoplax adhaerens, Nv - Nematostella vectensis, Hm - Hydra magnipapillata, Ce -Caenorhabditis elegans, Cb -Caenorhabditis briggsae, Dm -Drosophila melanogaster, Dp -Drosophila pseudoobscura, Ds - Drosophila simulans, Sp - Strongylocentrotus purpuratus, Bf - Branchiostoma floridae, Ci - Ciona intestinalis, Dr - Danio rerio, Xt - Xenopus tropicalis, Gg - Gallus gallus, Mm - Mus musculus, Hs -Homo sapiens.