Fig. 1. Domain structures of striatin family members.
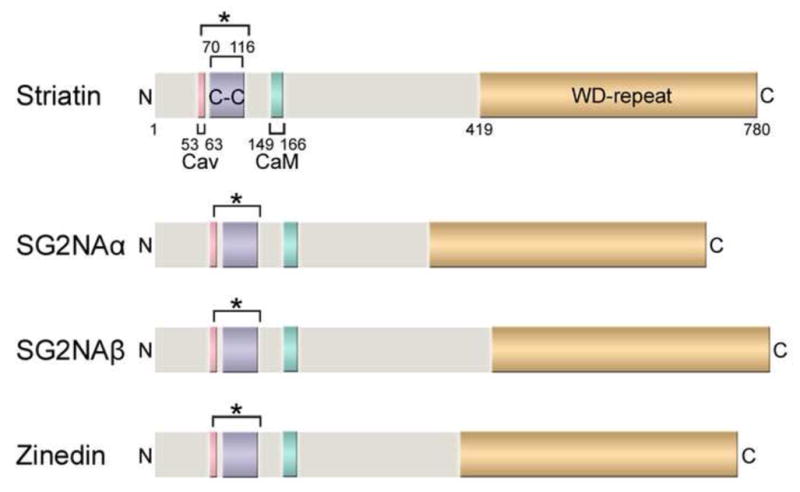
The domain structures of the human striatin family proteins, including striatin (780 amino acids), the two major isoforms of SG2NA (SG2NAα: 713 aa; SG2NAβ: 797 aa), and zinedin (753 aa), are shown drawn to scale. Four protein-protein interaction domains (labeled for striatin and color-coded for comparison in SG2NAα/β and zinedin) are highly conserved among the striatin family members and also throughout different species. Cav: Caveolin-binding domain; C-C: Coiled-coil domain; CaM: Ca2+-CaM-binding domain; WD-repeat: WD-repeat domain. The bracket with an asterisk (*) denotes the putative extended coiled-coil domain regions based on analyses using NCOILS and Paircoil2 algorithms (Gordon et al., 2011). Of note, some of the domains in SG2NA and zinedin are only predicted regions based on sequence comparisons and have not been experimentally verified.
