Fig. 5. Ccm3 forms different complexes by associating with alternative binding partners through its N- and C-terminal domains.
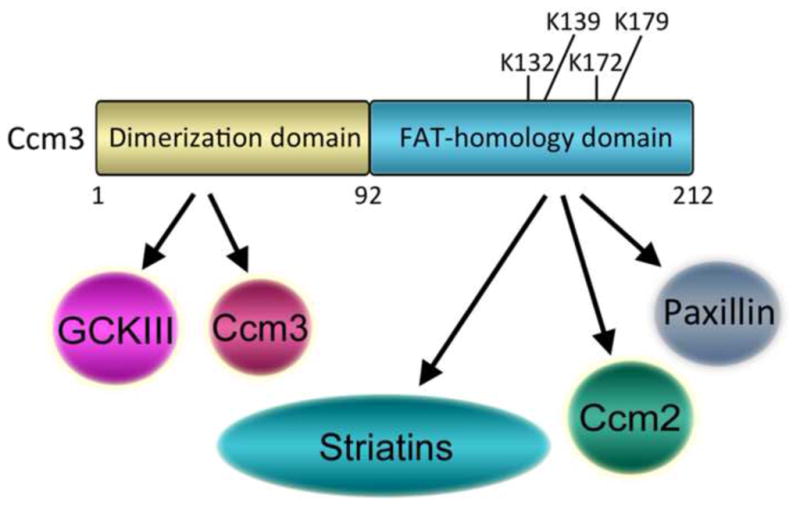
Ccm3 has a dimerization domain at its N-terminus and a FAT-homology domain at its C-terminus. The Ccm3 dimerization domain mediates homodimerization of Ccm3 proteins and binding of GCKIII kinases, two mutually exclusive events. The Ccm3 FAT-homology domain mediates binding of Ccm2, Paxillin, or striatin family members (striatins) to form multiple, independent complexes. Ccm3 may recruit GCKIII kinases to each of these complexes. Four lysines in the FAT-homology domain known to be important for complex formation with its binding partners are indicated.
