Figure 5.
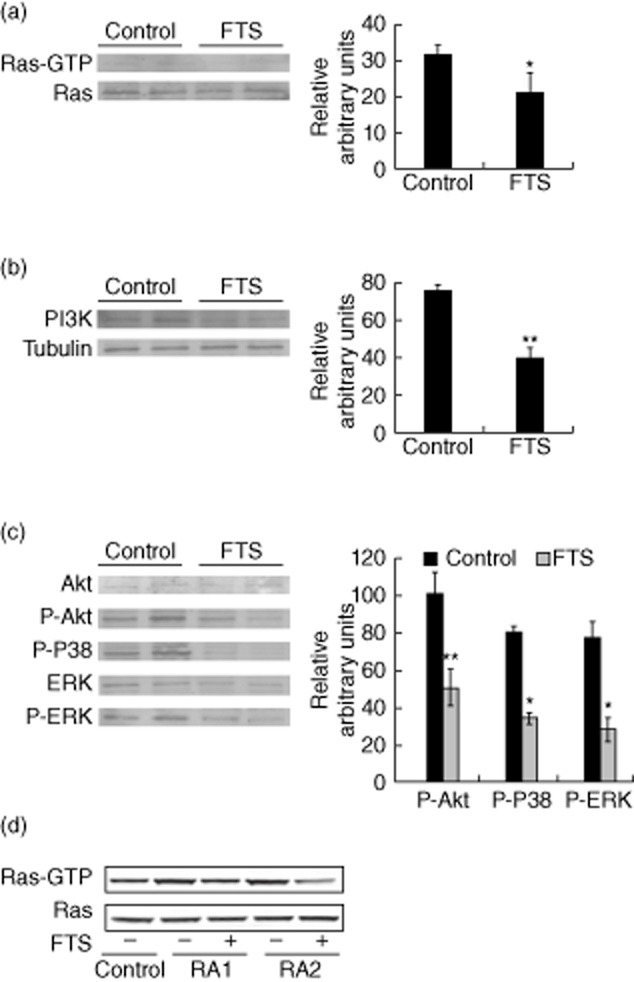
Farnesylthiosalicylic acid (FTS) reduces activation of protein kinase B (AKT), p38 and extracellular-regulated kinase (ERK) signalling and increases PI3K and forkhead box protein 3 (FoxP3) expression in rats with adjuvant-induced arthritis (AIA). (a,b,c). Inguinal lymph nodes (ILNs) of FTS-treated and control rats with AIA were tested for (a) guanosine triphosphate (GTP)-loaded Ras by glutathione S-transferase-rho binding domain (GST-RBD) pull-down assays, (b) PI3K expression, (c) phospho-AKT, phospho-p38 and phospho-ERK. Right panels show the results of densitometric analysis. (d) CD3+ lymphocytes from two rheumatoid arthritis (RA) patients were treated with FTS (50 μM) for 48 h and GTP-loaded Ras was studied by GST-RBD pull-down assay. *P < 0·05; **P < 0·01 compared to vehicle-treated control; Student's t-test. The following antibodies were used: anti-pan-Ras (Ab-3; Calbiochem), anti-PI3K (Millipore), anti-Akt, anti-phospho-Akt, anti-p38, anti-phospho-p38 (all from Cell Signaling), anti-ERK (Santa Cruz Biotechnology), anti-phospho ERK (Sigma-Aldrich), anti-tubulin and anti-FoxP3 (eBioScience).
