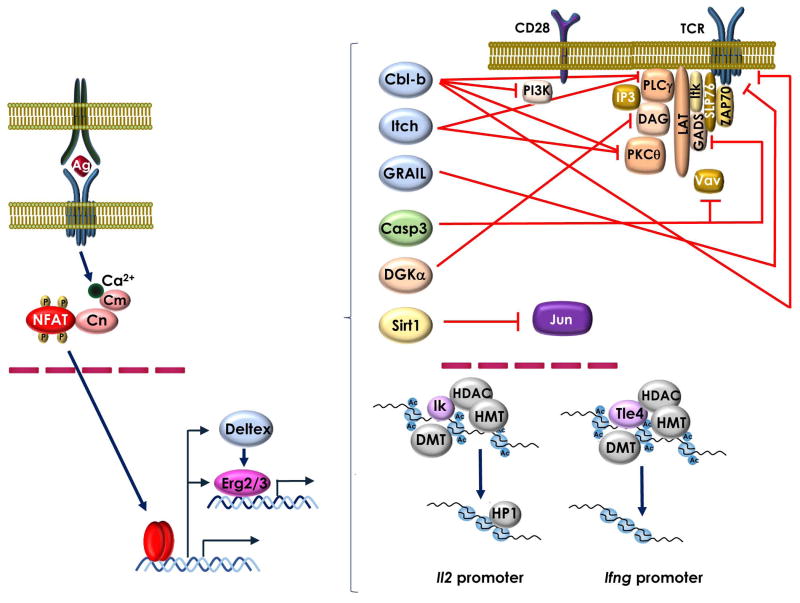
Figure 2.
NFAT proteins activate an anergy-inducing program of gene expression. In response to tolerizing stimuli, preferential activation of Ca2+-Calmodulin (Cm)-Calcineurin (Cn) signaling pathway leads to the expression of an NFAT-dependent program of gene expression. NFAT containing complexes, including NFAT1 homodimers, and other transcription factors, especially Egr proteins, will induce the expression of a series of proteins that will inhibit T cell activation at different levels. The ubiquitin ligases GRAIL, Itch and Cbl-b, caspase 3 and DGKα, will block TCR and CD28 signaling through targeted degradation or inactivation of multiple proteins that form part of the TCR signalosome. Sirt1 will directly deacetylate and inactivate Jun. Binding of transcriptional repressors, such as Ikaros (IK) or Tle4, to the Il2 and Ifng loci recruit chromatin remodeling proteins that together with DNA methyl transferases (DMT) will induce epigenetic modifications that will turn those genes into transcriptionally silenced loci.