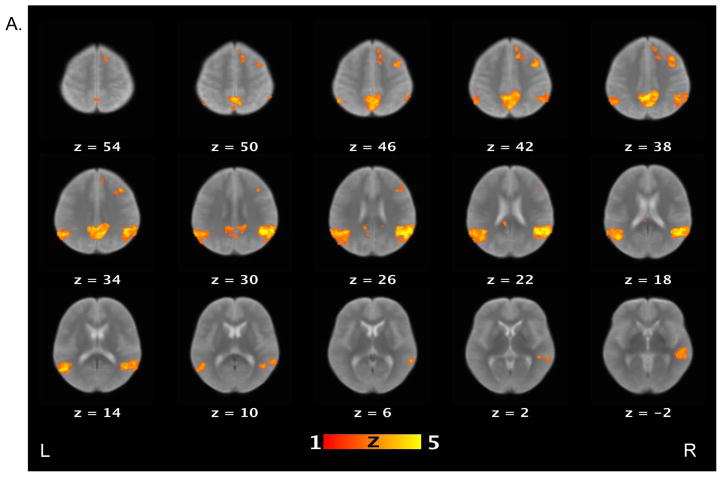
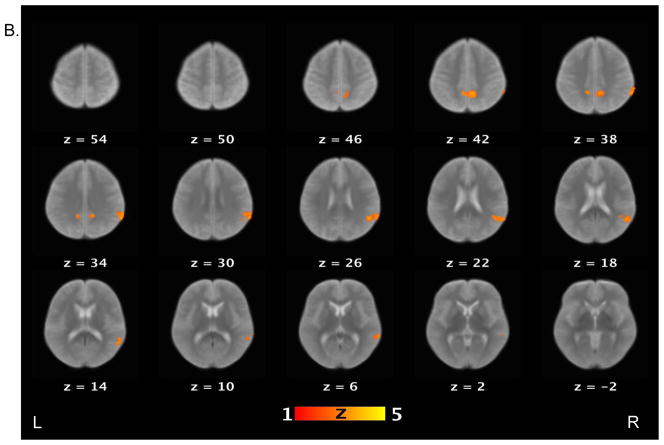
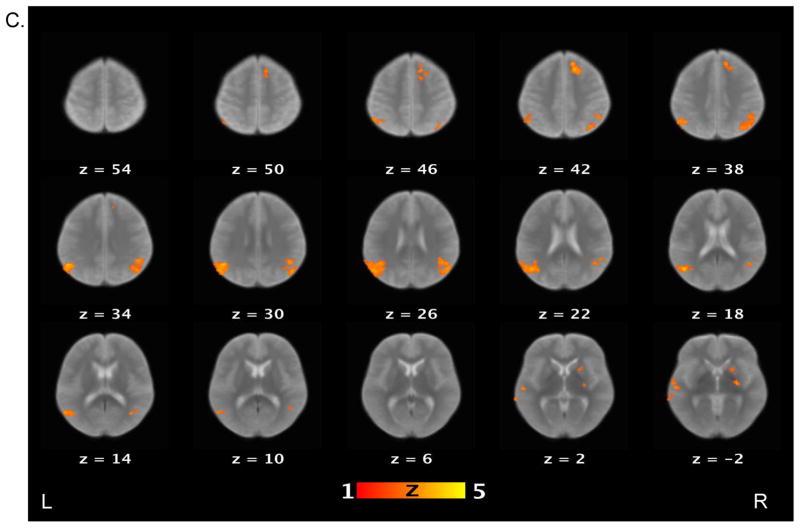
Figure 2.
Brain activations for the contrast of false belief versus simple reading conditions. Sections of brain templates with overlaid group analysis results of significant increase in signal intensity during false belief versus simple reading conditions in (A) controls, (B) schizophrenia patients, and (C) controls versus schizophrenia patients.