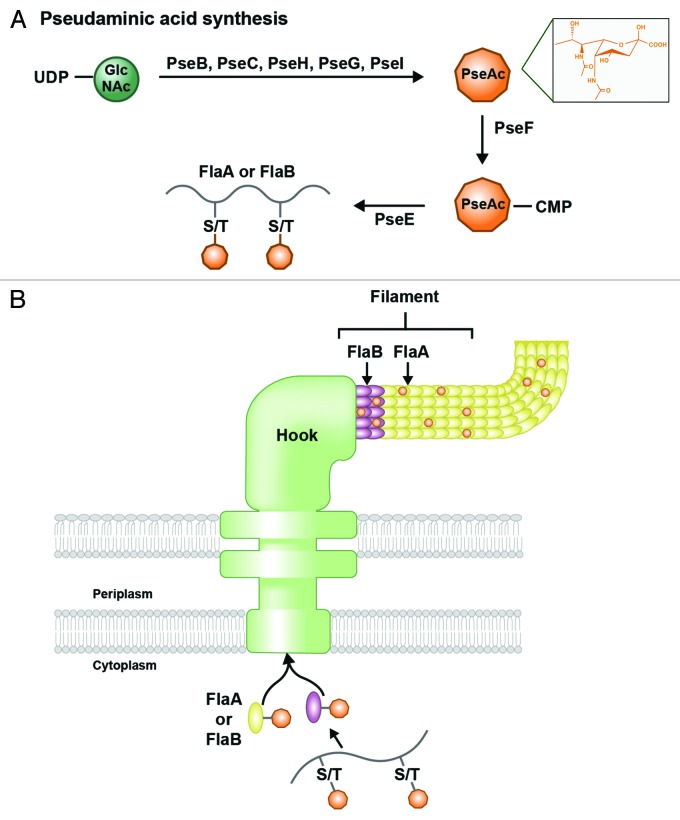
Figure 6. O-linked glycosylation of flagellar proteins in H. pylori. (A) Pseudaminic acid (PseAc) is synthesized in a five-step enzymatic process from a UDP-GlcNAc precursor. The structure of PseAc is shown (inset). It is then linked to a CMP nucleotide donor by PseF, and transferred by PseE from this donor to a serine or threonine residue on a FlaA or FlaB protein before the protein folds. (B) Glycosylated FlaA and FlaB proteins fold in the cytoplasm and display surface-exposed PseAc residues. Modified FlaA and FlaB are then translocated through the flagellar machinery to compose the flagellar filament. PseAc additions are apparent on both proteins within the filament.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.