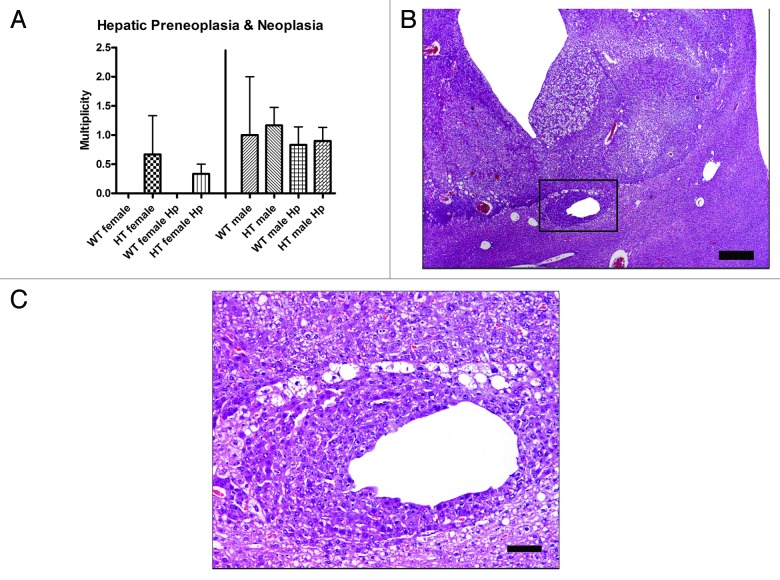
Figure 2. (A) Multiplicity of hepatic preneoplasia and neoplasia in the different groups of mice. (B) Hepatocellular carcinoma in a hepatitis C virus transgenic male mouse infected with H. pylori (HT male Hp). The tumor is poorly demarcated from the normal liver tissue and there is vacuolation of neoplastic cells and dilation of sinusoids. (C) Higher magnification (box in B) view of the junction between the poorly demarcated neoplasm and adjacent normal parenchyma. Neoplastic cells have cytoplasm with a deeper basophilic staining intensity and are often vacuolated. A focus of neoplastic cells also surrounds a distended hepatic sinusoid. (B) bar size 500 µm. (C) bar size 100 µm.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.