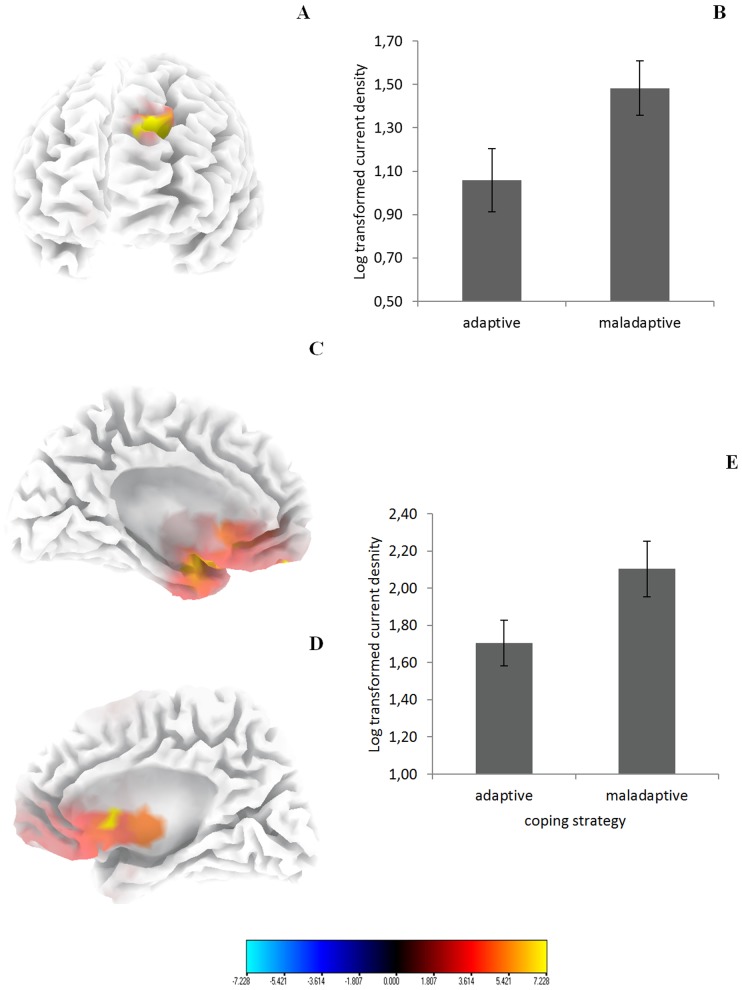
Figure 2.
(A) Increased activity in the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (BA9) for tinnitus patients using a maladaptive coping style in comparison to tinnitus patients using an adaptive coping style for the frequency band Alpha1. (B) Region of interest analysis shows increased activity in the left dorsolateral prefrontal cortex (BA9) for tinnitus patients using a maladaptive coping style in comparison to tinnitus patients using an adaptive coping style for Alpha1. (C & D) Increased activity in the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex (BA25) for tinnitus patients using a maladaptive coping style in comparison to tinnitus patients using an adaptive coping style for the frequency band Alpha2. (E) Region of interest analysis shows increased activity in the subgenual anterior cingulate cortex (BA25) for tinnitus patients using a maladaptive coping style in comparison to tinnitus patients using an adaptive coping style for Alpha2.