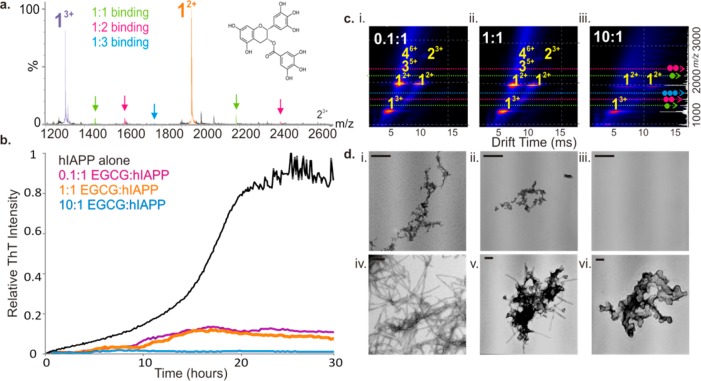
Figure 5.
Inhibition of hIAPP fibril formation by EGCG. (a) Positive ion ESI mass spectrum showing binding of EGCG (added at 500 μM to 50 μM peptide) to both the 2+ (orange) and 3+ (purple) charge state ions of hIAPP monomer. Stoichiometry of binding is shown by color: 1:1 inhibitor molecule bound to an IAPP monomer is highlighted in green, 2:1 in pink, and 3:1 in blue. EGCG is shown as an inset. (b) ThT fluorescence intensity of hIAPP (black) (50 μM peptide, 20 mM ammonium acetate buffer, pH 6.8, 37 °C, 600 rpm) with increasing EGCG:hIAPP molar ratios: 0.1:1 (pink), 1:1 (orange), and 10:1 (blue). (c) ESI-IMS-MS driftscope plots of hIAPP oligomers formed in the presence of (i) 0.1:1, (ii) 1:1, and (iii) 10:1 molar ratios of EGCG:peptide monomer at t = 5 h. The number of EGCG molecules bound to each species is shown as a colored dot. (d) Negative stain TEM images of hIAPP incubated with (i) 0.1:1, (ii) 1:1, and (iii) 10:1 molar ratios of EGCG for 5 days (37 °C, 600 rpm). (iv) hIAPP fibrils alone and aggregates formed when a 10-fold molar excess of EGCG:hIAPP is added to preformed hIAPP fibrils after 5 h (v) and 24 h (vi). Scale bar is 100 nm.