Figure 4.
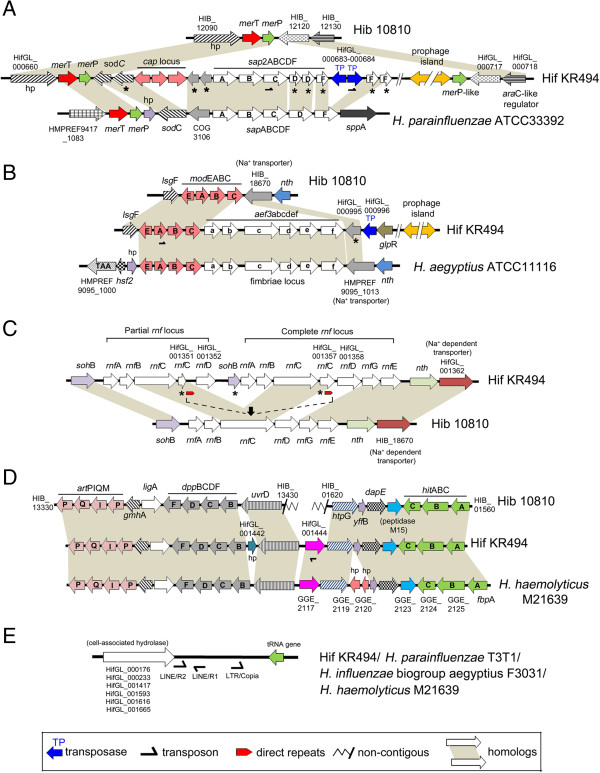
Genomic structures and organizations of unique genes in H. influenzae type f KR494. Organization of loci of specific genes in Hif KR494 were compared with reference strains or closely-related species. Genomes of respective reference species or strains are indicated on the right hand side of each panel. The flanking genes and genomic organization of (A) sap2ABCDF, (B) fimbriae gene cluster aef3abcdef, (C) duplet rnf electron transport complex, (D) unique iron-binding transporter HifGL_001444, and (E) genetic island structure of cell wall-associated hydrolase of KR494, were analogous to the indicated reference species while the unique genes were absent from Hib 10810 (a representative of H. influenzae reference genomes). Asterisks indicate partial CDSs. Hypothetical proteins of unknown function are denoted as “hp”. Homologous genes are indicated with gray shading. In panel (A), the predicted protein products of sap2D and sap2F (ATPase subunits) are shorter than their counterparts in H. parainfluenzae. The loss of a functional ATPase complex (sap2DF) might be compensated by the subunit product (SapD and SapF) from the H. influenzae conserved Sap system. In panel (C), two identical 41 bp direct repeats were identified at 40 bp upstream of HifGL_001352 (rnfD) and at the first 220 bp of HifGL_001357 (rnfC), respectively. The repeats may mark the two edges of the inserted genomic fragment suggesting the intergenic region between HifGL_001351 and HifGL_001358 as the insertion site. The black arrow indicates the possible insertion at the original rnfC subunit gene. The insertion may also have resulted in partial CDSs of the neighboring loci, HifGL_001351 and HifGL_001357. Both loci encode rnfC but with internal stop codon thus may not encode a functional protein. Nevertheless, the functionality of the rnf operon might not be affected since the intact CDS of rnfC were retained at HifGL_001350 and HifGL_001356.
