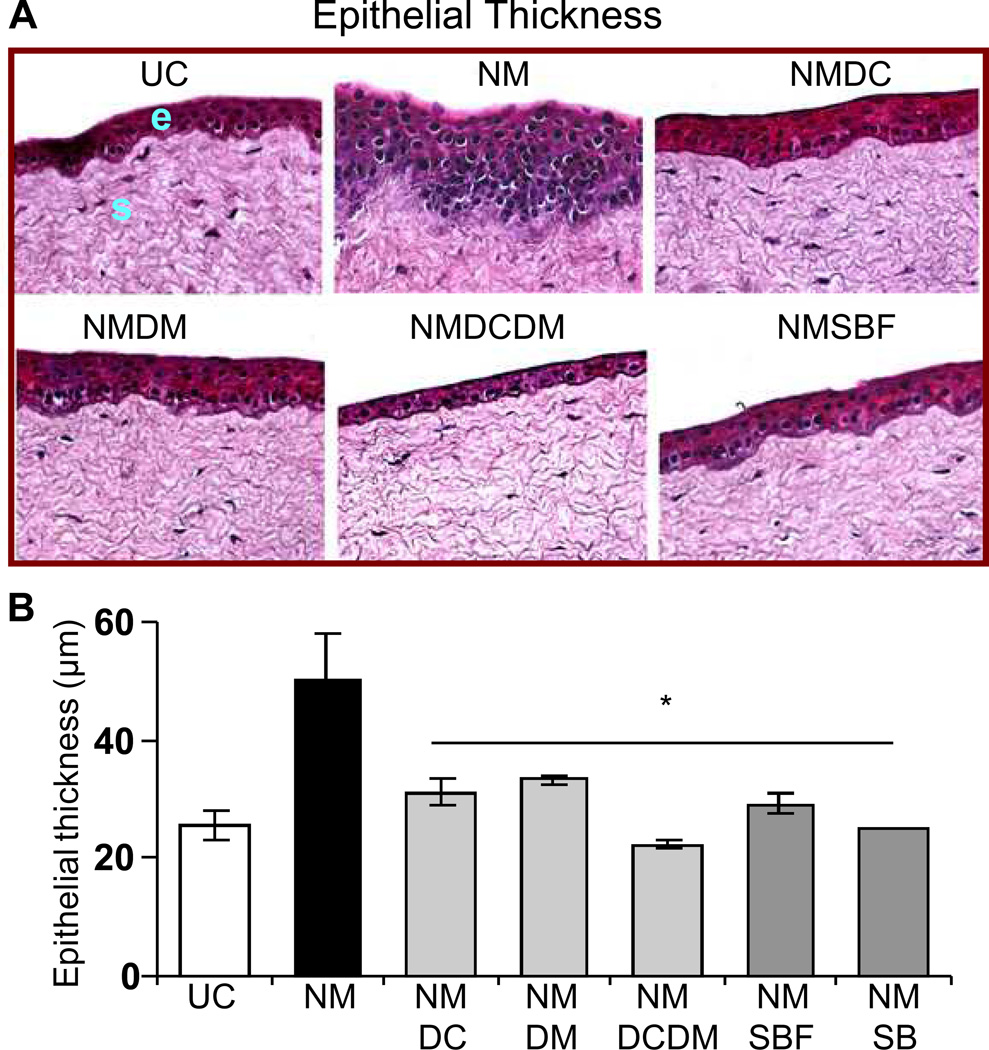
Figure 2.
Effect of doxycycline, dexamethasone treatments alone or in combination, and silibinin or silibinin formulation treatments on NM-induced epithelial thickness in cultured rabbit eye cornea. The dissected rabbit corneas in culture were either untreated (UC), or treated with 10 µl of the agents drop wise on the central cornea after 2 h and every 4 h thereafter, for 24 h following 100 nmol NM exposure as detailed under ‘Materials and Methods’. Following the NM exposure and treatments, the corneas were fixed, five µm sections were H&E stained and evaluated for the histopathological changes. Representative H&E stained sections are shown in A. The epithelial thickness (µm) was measured randomly in at least five fields per tissue sample from two sets of H&E stained slides (×400 magnification; B) as detailed under ‘Materials and Methods’. Data presented are mean ± SEM (n=3). *, p<0.05 as compared to respective NM exposed group. e, epithelial layer; s, stroma; UC, untreated control; NM, nitrogen mustard; NMDC, nitrogen mustard+doxycycline; NMDM, nitrogen mustard+dexamethasone; NMDCDM, nitrogen mustard+doxycycline +dexamethasone; NMSBF, nitrogen mustard+silibinin formulation; NMSB, nitrogen mustard+silibinin in DMSO.