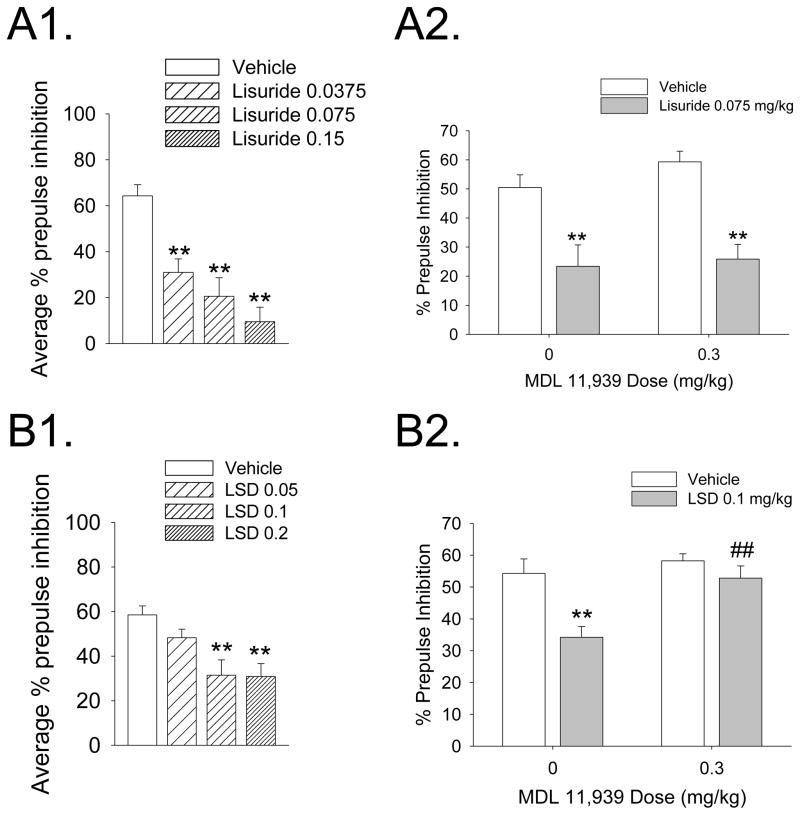
Figure 3.
Effects of lisuride (A) and LSD (B) on prepulse inhibition in rats. (A1) Effect of lisuride (0.0375, 0.075, and 0.15 mg/kg, s.c.) on average prepulse inhibition. (A2) Effects of the selective 5-HT2A antagonist MDL 11,939 on the disruption of PPI induced by lisuride. (B1) Effect of LSD (0.05, 0.1, and 0.2 mg/kg, s.c.) on average prepulse inhibition. (A2) Effects of the selective 5-HT2A antagonist MDL 11,939 on the disruption of PPI induced by LSD. Values represent mean ± SEM for each group. Drug doses are in milligram per kilogram. *p < 0.05, **p < 0.01, significantly different from vehicle control; ##p < 0.01, significantly different from LSD-treated animals. Male Sprague-Dawley rats (250–275 g) were placed in a stabilimeter chamber 30 min after treatment with MDL 11,939, 10 min after treatment with lisuride hydrogen maleate, or 5 min after treatment with LSD tartrate. After a 5-min acclimation period to 65-dB broadband background noise, %prepulse inhibition was assessed using a combination of startle trials (a 40-ms 120-dB pulse of broadband white noise) and prepulse trials (a 20-ms acoustic prepulse at either 68, 71, or 77 dB, an 80-ms delay, and then a 40-ms 120-dB startle pulse) presented in a pseudo-randomized order. Data from: Halberstadt and Geyer, 2010.