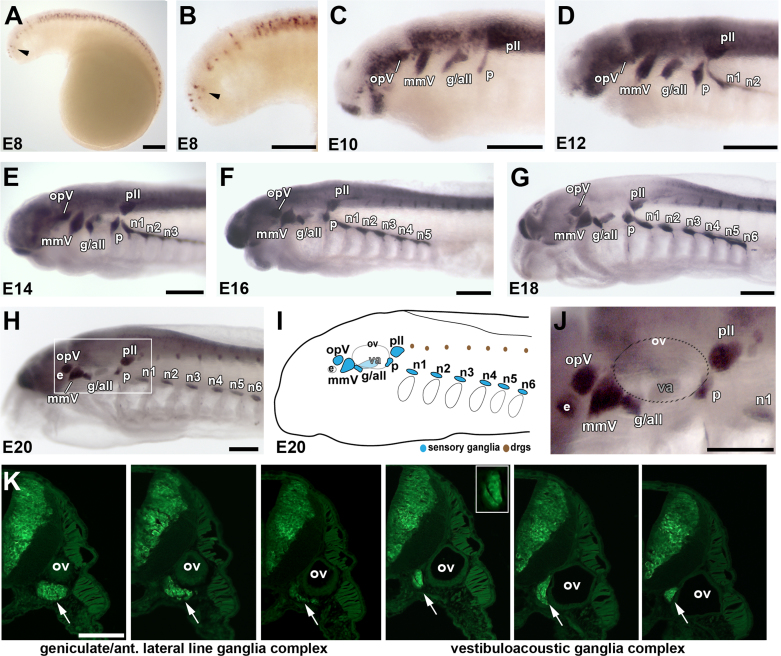
Fig. 1.
Spatiotemporal development of lamprey cranial sensory ganglia. Anterior is to the left for all whole-mount images. (A) and (B) Low-power (A) and higher-power view (B) of an embryo at embryonic day 8 (E8) immunostained for the pan-neuronal Elav-family members HuC/D (Hu). HuC/D expression is strong in neurons within the neural tube, with fainter expression in neurons lateral to the rostral neural tube (arrowhead). (C) By E10, discrete lateral patches of HuC/D expression reveal the primordia of all cranial sensory ganglia except the nodose: the ophthalmic trigeminal ganglion (opV), the maxillomandibular trigeminal ganglion (mmV), the geniculate/anterior lateral line ganglionic complex (g/all), the petrosal ganglion (p) and the posterior lateral line ganglion (pll). (D)–(G) HuC/D immunostaining of embryos at E12 (D), E14 (E), E16 (F) and E18 (G) shows the development of the six nodose ganglia in a rostrocaudal sequence dorsal to the branchial arches and the progressive condensation of all the cranial ganglia. Dorsal root ganglia are also visible from E16, adjacent to the dorsal neural tube. (H)–(J) By E20, all the cranial sensory ganglia have formed. (H) Low-power and (I) schematic view of an E20 embryo, showing the location of cranial sensory ganglia [blue in (I)] and dorsal root ganglia [brown in (I)]. (J) A higher-power view of the boxed area in (H), showing distinct opV and mmV ganglia, the geniculate/anterior lateral line ganglionic complex, the vestibuloacoustic ganglion (medial to the otic vesicle, hence hardly stained in whole-mount), the petrosal ganglion, the posterior lateral line ganglion and the most rostral nodose ganglion (n1). (K) Transverse serial sections immunostained for HuC/D (green), starting near the rostral edge of the otic vesicle [see panel (J) for orientation of otic vesicle, which is indicated by a dotted oval] and progressing caudally through the geniculate/aLL ganglionic complex ventral to the otic vesicle (arrow, left-hand three images) and then the vestibuloacoustic ganglion medial to the otic vesicle (arrow, right-hand three images). In the fourth and fifth images, the developing intracapsular ganglion (second ganglion of the anterior lateral line nerve) may also be visible, medial to the vestibuloacoustic ganglion and slightly separated from it by a thin HuC/D-negative space (inset). Abbreviations: all, anterior lateral line ganglion; drgs, dorsal root ganglia; e, eye; g, geniculate ganglion; mmV, maxillomandibular trigeminal ganglion; n, nodose ganglion; opV, ophthalmic trigeminal (profundal) ganglion; ov, otic vesicle; p, petrosal ganglion; pll, posterior lateral line ganglion; va, vestibuloacoustic ganglion. Scale bars: (A)–(J) 0.2 mm; (K) 50 μm.