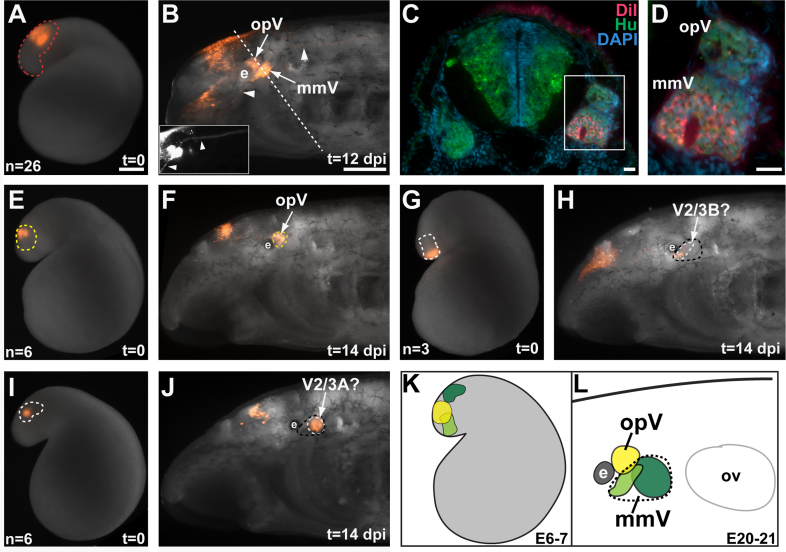
Fig. 4.
Fate-mapping of opV and mmV placode-derived neurons reveals two separate domains of mmV neuron precursors at late neurula stages. Anterior is to the left for all whole-mount images. (A) An E6.5 embryo immediately after DiI injection into a broad patch of anterodorsal head ectoderm within the region outlined in red, which contains both opV and mmV neuron precursors. (B) The same embryo as in (A) at E18 (t=12 dpi), showing DiI labeling in the opV and mmV ganglia. DiI is also visible in the upper lip-innervating mmV nerve (V2/3A, inset, ventral arrowhead) and central projections from the mmV ganglion (inset, dorsal arrowhead). Dotted line shows plane of section in (C) and (D). (C) Merged images of low-power and (D) higher-power views of an oblique section through both the opV and mmV ganglia, immunostained for the neuronal marker HuC/D (green) and counterstained for the nuclear marker DAPI (blue), showing DiI (red) in surface ectoderm and also co-localized with neurons (HuC/D, green) in both the opV and mmV ganglia. (E) An E6.5 embryo immediately after focal DiI injection into the region of head ectoderm outlined in yellow, which contains opV neuron precursors. (F) The same embryo as in (E) at E20 (t=14 dpi), showing restriction of DiI to the opV ganglion. (G) An E6.5 embryo immediately after a focal DiI injection into the region of head ectoderm outlined in white (shaded light green in schematic). (H) The same embryo as in (G) at E20 (t=14 dpi), showing DiI localization to a relatively small, rostral domain (outlined in white) of the mmV ganglion (outlined in black), which may correspond to lower lip/velum-innervating V2/3B neurons (see text). (I) An E6.5 embryo immediately after a focal DiI injection into the region of head ectoderm outlined in white (shaded dark green in schematic). (J) The same embryo as in (I) at E20 (t=14 dpi), showing DiI localization to a larger, caudal domain (outlined in white) of the mmV ganglion (outlined in black), which may correspond to upper lip-innervating V2/3A neurons (see text). (K) Schematic fate-map at E6–7 summarizing the location of opV neuron precursors (yellow) between two separate patches of mmV neuron precursors (light and dark green). (L) Schematic summarizing the fate at E20–21 of DiI-injected cells within the locations shown in panel (K). The opV ganglion (yellow) lies dorsal to the mmV ganglion (dotted black outline). Rostral (light green) and caudal (dark green) subregions of the mmV ganglion are distinguishable in the E6–7 fate-map, which may correspond to V2/3B and V2/3A neurons, respectively (see text). Abbreviations: dpi, days post-injection; e, eye; mmV, maxillomandibular trigeminal ganglion; opV, ophthalmic trigeminal ganglion; ov, otic vesicle; t, time, V2/3A, upper lip-innervating trigeminal neurons; V2/3B, lower lip/velum-innervating trigeminal neurons. Scale bars: (A), (E), (G) and (I) 0.2 mm; (B), (F), (H) and (J) 0.2 mm; (C) and (D) 10 μm.