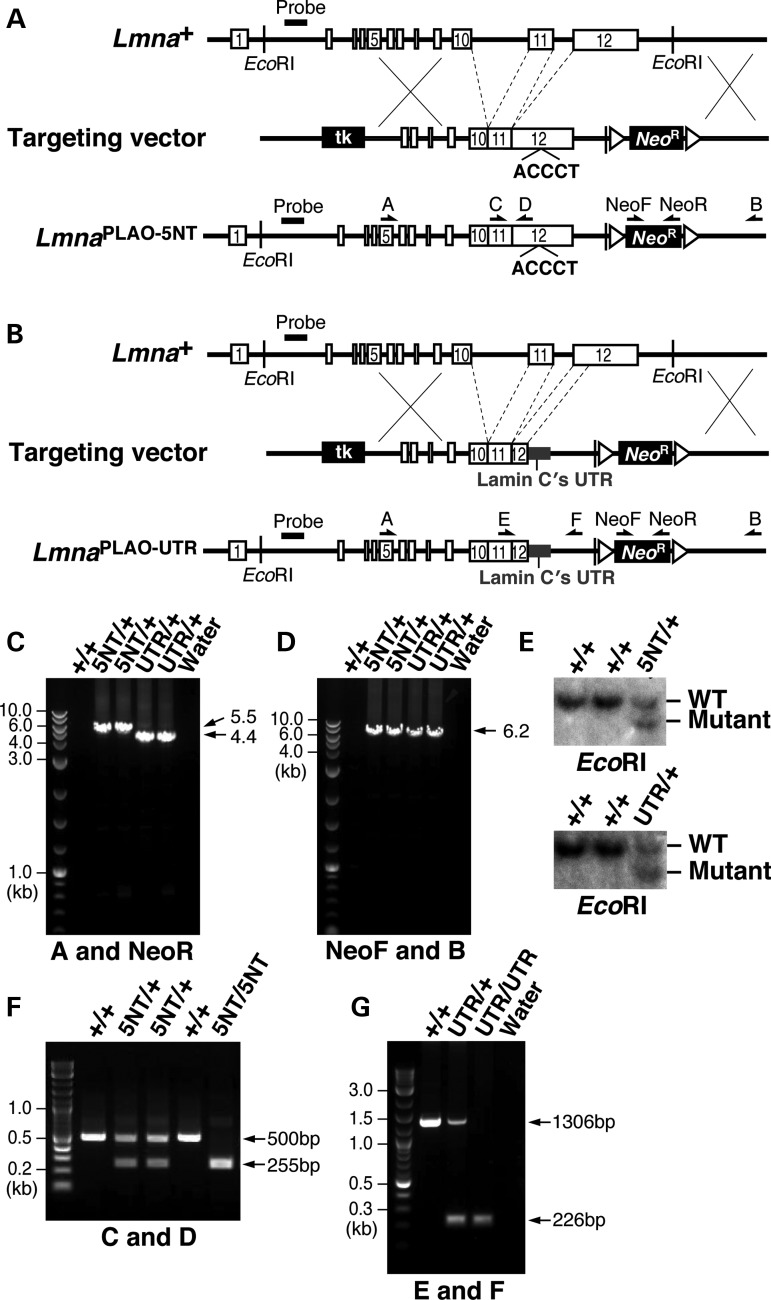
Figure 1.
Knock-in mice expressing prelamin A transcripts with mutations in the 3′ UTR. (A) Strategy to create the LmnaPLAO-5NT allele, in which 5-nt of the seed-binding sequence in a predicted miR-9 binding site in prelamin A's 3′ UTR (CCAAAG) (5) were replaced with ACCCTG. Introns 10 and 11 were also deleted; consequently, the targeted allele yields exclusively prelamin A (and no lamin C) (11). Exons are depicted as white boxes; loxP sites are represented by arrowheads; the position of the 5′ flanking probe and EcoRI sites for Southern blotting are also identified. Primer locations for the 5′ (primers A and NeoR) and 3′ (primers NeoF and B) long-range PCRs and genotyping PCRs (primers C and D) are indicated with arrows. (B) Strategy to create the Lmnaplao-utr allele, in which prelamin A's 3′ UTR was replaced with lamin C's 3′ UTR (grey). Introns 10 and 11 were deleted. Primer locations for the 5′ (primers A and NeoR) and 3′ (primers NeoF and B) long-range PCRs and genotyping PCRs (primers E and F) are indicated with arrows. (C) The 5′ long-range PCRs with the LmnaPLAO-5NT and Lmnaplao-utr alleles yield 5.5 kb (lanes 3 and 4) and 4.4 kb (lanes 5 and 6) fragments, respectively. No PCR product was amplified from wild-type DNA (lane 2). (D) The 3′ long-range PCRs with the LmnaPLAO-5NT and Lmnaplao-utr alleles yield a 6.2 kb fragment (lanes 3–6); no product was amplified from wild-type DNA (lane 2). (E) Southern blot analysis to identify targeted mouse ES cell clones for the LmnaPLAO-5NT and Lmnaplao-utr alleles. Genomic DNA was digested with EcoRI, and the blot was hybridized with a 5′ flanking probe (A and B). (F) Genotyping PCR for the LmnaPLAO-5NT allele yields a 255 bp fragment, whereas wild-type DNA yields a 500 bp fragment. (G) Genotyping PCR with the Lmnaplao-utr allele yields a 226 bp fragment, whereas wild-type DNA yields a 1.3 kb fragment.