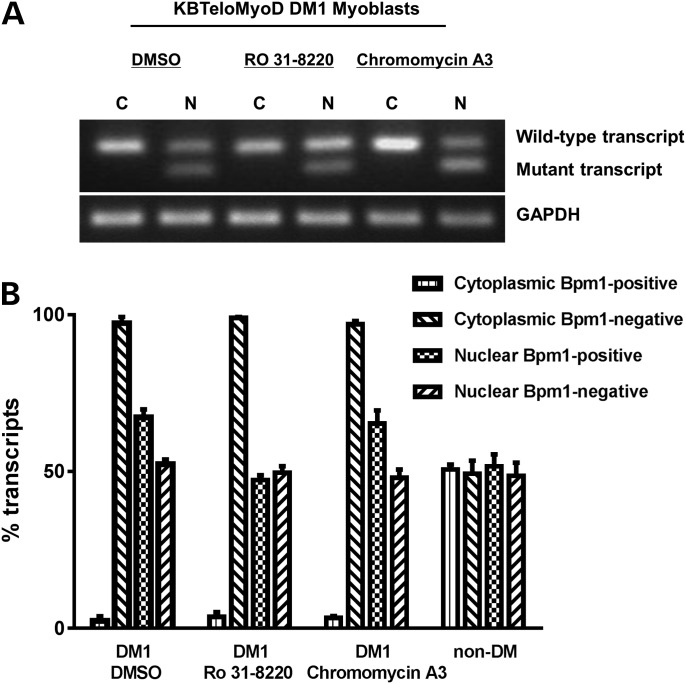
Figure 5.
The effect of compound treatment on repeat expansion transcripts. The relative proportions of the mutant and wild-type DMPK transcripts in KBTeloMyoD differentiated fibroblast cells (DM1) were assessed following treatments with Ro 31-8220 (10 μm), chromomycin A3 (40 nm) and DMSO control. (A) Ethidium bromide-stained gel showing RT–PCR products from nuclear (N) and cytoplasmic (C) RNA fractions of KBTeloMyoD cells following the amplification and BpmI restriction enzyme digestion of a fragment of DMPK. GAPDH is used as a loading control. (B) Histograms showing the relative proportions of mutant (BpmI positive) and wild-type (BpmI negative) nuclear DMPK transcripts expressed as a percentage of the total nuclear DMPK transcripts. Quantitative RT–PCR was conducted using Genescan analysis of areas under the peaks following amplification of DMPK and BpmI restriction enzyme digestion.