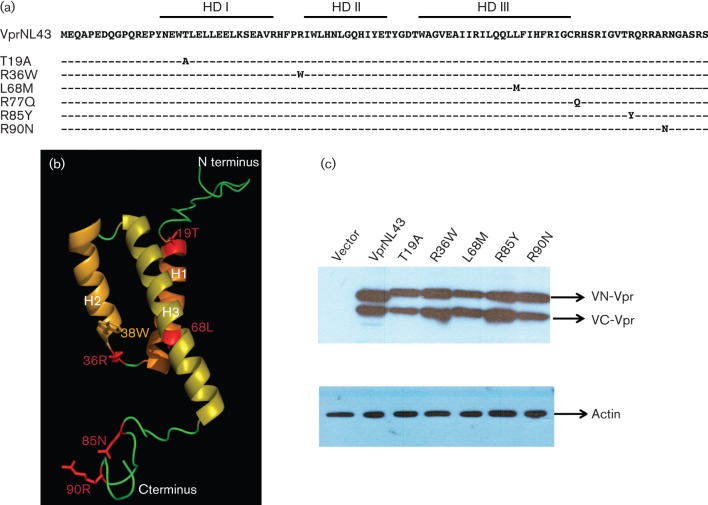
Fig. 2.
Construction and characterization of expression plasmids representing HIV-1 Vpr variants from LTNP and RP subjects. (a) Schematic depicting Vpr variants selected for analysis from the frequency analysis shown in Table 1. Mutations introduced in the VprNL43 background are shown in their respective amino acid positions as Venus split constructs with an HA-tag. (b) Three dimensional structure of Vpr representing residues from LTNP and RP subjects. The overall structure of Vpr consists of three helices (H1–H3) and the N- and C-terminal regions (shown in green). Vpr variants used in this study are shown in red. (c) Expression of Venus-C (VC-) Vpr and Venus-N (VN-) Vpr variants was assessed by transfecting HEK293T cells with VN-Vpr and VC-Vpr variant expression plasmids or control plasmid. Forty eight hours post-transfection cell lysates were harvested and Vpr expression levels verified by immunoblot against the HA antibody. Actin was probed as loading control. The figure represents one of five independent experiments.