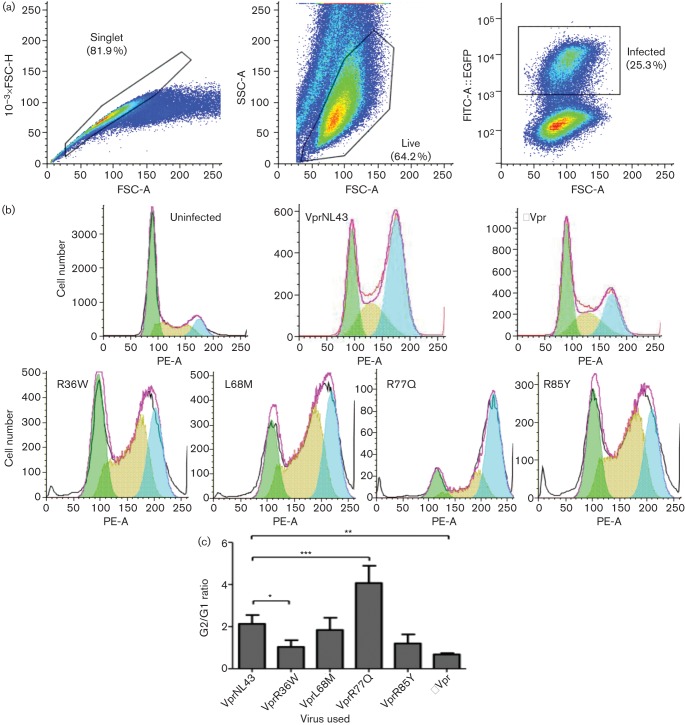
Fig. 5.
Evaluation of cell cycle arrest induced by HIV-1 expressing Vpr variants. (a) Gating strategy used to assess Vpr induced cell cycle arrest by flow cytometry in Jurkat cells infected with HIV-1 EGFP reporter virus expressing representative Vpr variants from LTNPs and RPs. Seventy-two hours post-infection cells were collected, fixed and stained with propidium iodide, and analysed by flow cytometry. (b) Cell cycle analysis of HIV-1 wild-type, HIV-1 ΔVpr and HIV-1 Vpr variant virus infected Jurkat cells. The EGFP positive cells were analysed for their cell cycle profiles, which were then fitted to a peak distribution for the relative proportion of cells in the G0 and G2 cell phases. Results represent the cell cycle distributions for each of the Vpr variants tested, and the figure represents one of three independent experiments. (c) Significance testing was performed using Student’s t-test comparing each Vpr variant with the wild-type (NL43) control. The graph represents the mean of three independent experiments. *P<0.05, **P<0.01, ***P<0.001. Error bars represent ±se/sd.