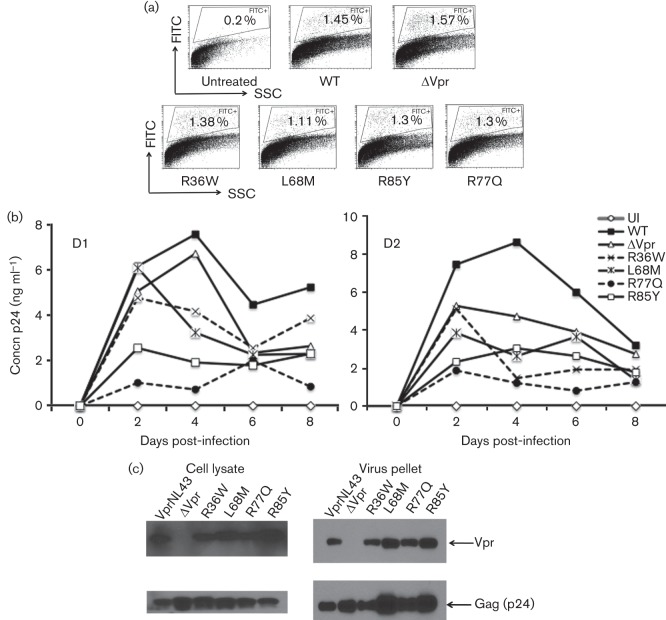
Fig. 6.
Replication kinetics of HIV-1 containing Vpr variations associated with LTNPs and RPs compared with wild-type Vpr. (a) PBMCs infected with NL43 EGFP reporter virus expressing various Vpr mutants were assessed by flow cytometry to quantify the productively infected cells by gating the EGFP positive cells. EGFP positive cells (%) are gated and marked. ‘Untreated’ represents uninfected (UI) cells and Vpr mutants are marked on the x-axis. The figure represents results from one of three experiments using different donors. (b) Replication kinetics in PBMCs infected with NL43 virus containing Vpr mutations were measured. The Vpr mutants (R36W, L68M, R77Q and R85Y) are mutations introduced in the VprNL43 background. PBMCs were infected with 0.1 m.o.i. virus and the supernatants were collected at 2 day intervals and assessed for p24. Representative viral replication kinetics are presented from two independent donors. A similar replication pattern was observed in multiple donors (n = 4). (c) Virus containing Vpr variants were tested for Vpr expression in virus particles and cell lysates by transfecting HEK293T cells with WT and mutant proviral DNA constructs. Supernatants and cell lysates harvested 72 h post-transfection were subjected to immunoblot against Vpr and Gag. Panels represent Vpr and Gag expression in cell lysates and virus particles.