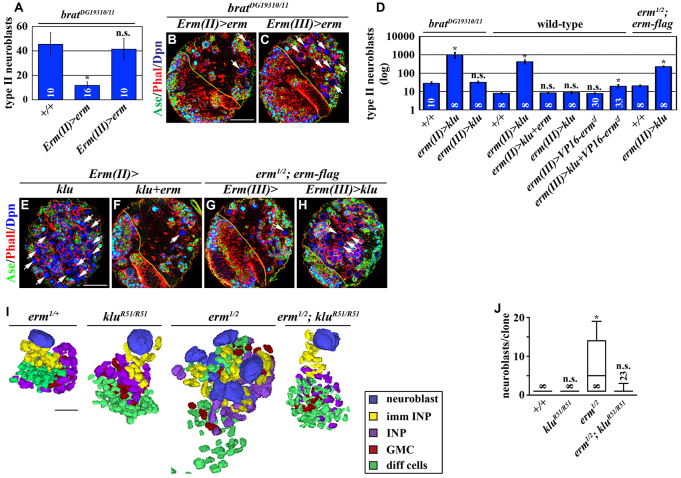
Fig. 4.
Erm-dependent restriction of developmental potential in immature INPs leads to attenuated competence to respond to Klu in INPs. (A-C) Overexpression of erm in Ase- immature INPs can suppress the supernumerary neuroblast phenotype in brat hypomorphic brains as seen in B and C. Scale bar: 40 μm. (A) Quantification of total type II neuroblasts (Dpn+Ase-) per brain lobe of the indicated genotypes. (D-H) Co-expression of erm can suppress the supernumerary neuroblast phenotype induced by mis-expression of klu, as seen in E-H. Scale bar: 40 μm. (D) The quantification of total type II neuroblasts (Dpn+Ase-) per brain lobe of the indicated genotypes. (I,J) Removing klu function suppresses supernumerary neuroblast formation in erm-null brains. (I) Three-dimensional reconstructed images of clones of the genotype indicated. Third instar larval brains carrying GFP-marked mosaic clones derived from single neuroblasts of the genotype indicated were stained for GFP, Dpn, Ase, Pros and Elav. Scale bar: 10 μm. (J) Quantification of total type II neuroblasts (Dpn+Ase-) per clone for the indicated genotypes.