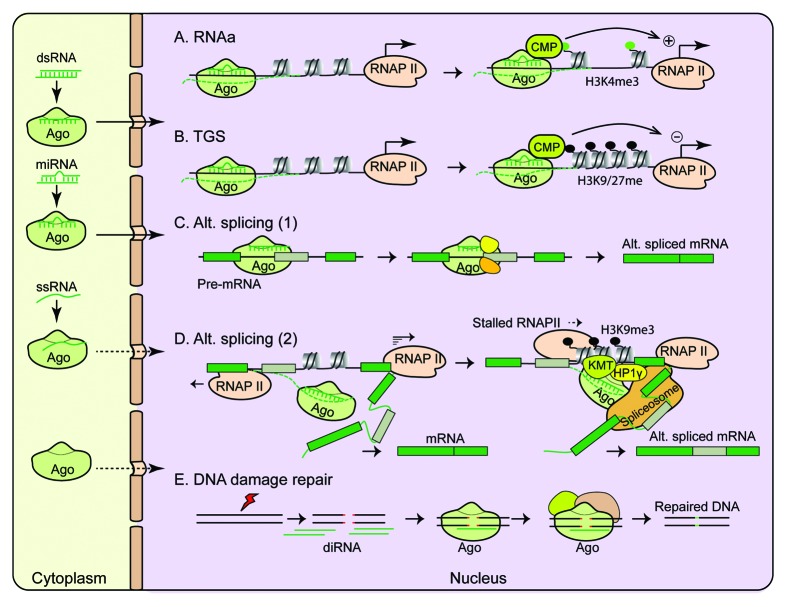
Figure 1. Multi-functional roles of nuclear Ago proteins. Cytoplasmic Agos enter the nucleus through nuclear import pathways (e.g., importin 8) via one of the four possible routes as depicted in the left panel of the figure: in complex with a guide dsRNA, miRNA, ssRNA, or as a free form. In the nucleus, they are guided by the bound RNA to its homologous target sites or recruited by nuclear-localized RNAs to chromatin sites to exert multi-functional roles. (A and B) Ago-mediated chromatin modification processes. (A) RNAa: Recruitment of CMPs by Ago-dsRNA or miRNA complex leads to increased active chromatin marks such as H3K4me3 methylation, allowing active transcription to occur at the targeted promoter. (B) TGS: Recruitment of CMPs by Ago-dsRNA or miRNA complex leads to increased repressive chromatin marks such as H3K9/K27 methylation thereby inhibits transcription at the targeted promoter. (C and D) RNA-mediated alteration of splicing. (C) Exogenous dsRNA-guided alternative splicing: dsRNA-Ago complex forces exon exclusion or inclusion by targeting intronic or exonic sequences involved in splicing. (D) Endogenous small RNA-mediated alternative splicing: Agos, possibly guided by unstructured single stranded small RNA (ssRNA), are recruited to chromatin at the 3′ ends of the variant regions possibly by an intragenic antisense transcript. Interactions with other chromatin components (such as HP1γ or SR proteins) result in H3K9me3 mark deposition by Suv39h1 and EHMT2 (KMT lysine methyl transferase). Consequently, RNAP II elongation rate is slowed, which in turn facilitates spliceosome recruitment and allows alternative splicing of the variant exons. (E) DNA damage repair process. diRNAs generated from DSBs are incorporated into Ago proteins which facilitate DNA damage repair by directly interacting with repair proteins or by affecting local chromatin structures via recruitment of CMPs. CMPs, chromatin modifying proteins; diRNAs, double-strand-break-induced small RNAs; DSBs, double strand breaks; dsRNAs, double stranded RNAs; miRNA, microRNA; RNAa, RNA activation; RNAP II, RNA polymerase II; ssRNA, single stranded small RNA; TGS, transcriptional gene silencing.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.