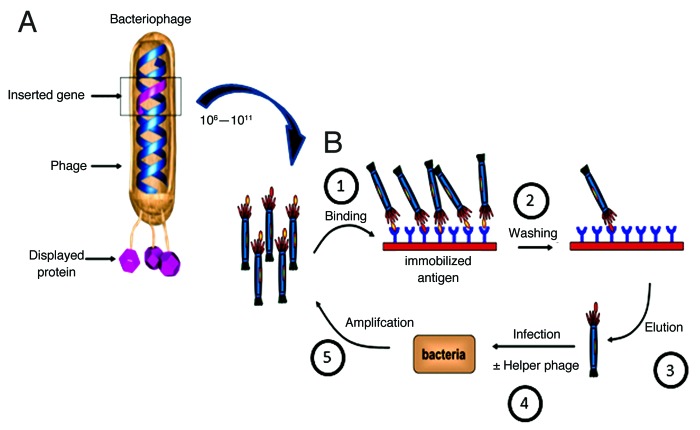
Figure 1. Phage display and selection. (A) A bacteriophage highlighting the genotype-phenotype coupling that is fundamental to phage display technology. The gene of interest (pink) is cloned into the gene 3 protein (g3p) of phage DNA, which results in the display of the pink protein product (antibody, peptide) on the surface of the phage as a polypeptide fusion. (B) Overview of phage display selection process. (1) A phage library containing 10^6-10^11 clones is incubated with immobilized antigen. (2) Unbound phage are removed by washing. (3) Bound phage are eluted. (4) E.coli are infected with eluted phage with or without helper phage to amplify eluted candidates. (5) Cells are plated onto selective plates and amplified. Process is reiterated 2–3 times resulting in enriched population of antibody/peptide fragments for the antigen of interest. Additional site directed mutagenesis or depletion approaches can be used to further tune desired antibody properties. Adapted and reproduced with permission from Buckler D, Schofield D, Sexton DJ, Lowe D and Vaughan TJ. Selection and screening of antibody phage display libraries. In: Wood CR, ed. Antibody Drug Discovery.©2012 World Scientific Publishing Co.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.