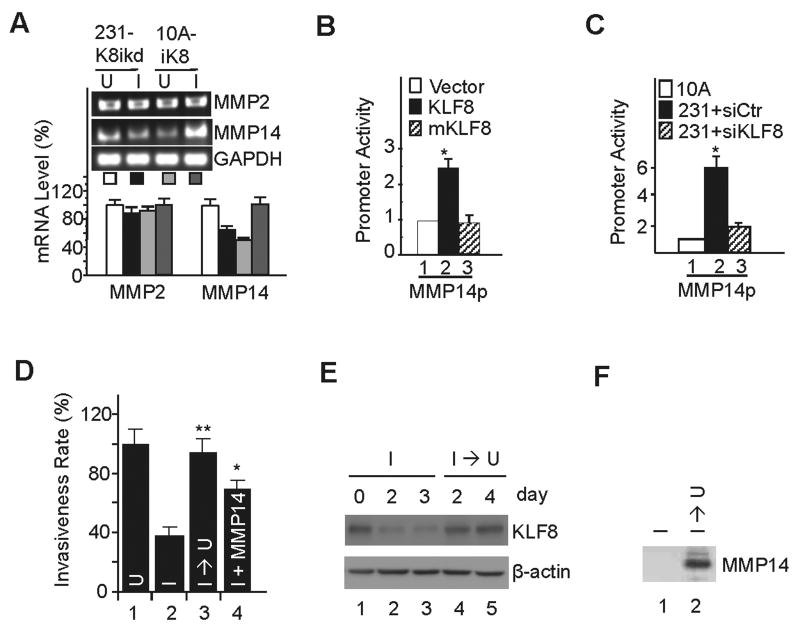
Figure 1.
KLF8 upregulation of MMP14 is critical for breast cancer cell invasiveness. A, KLF8 promotes mRNA expression of MMP14 but not MMP2. The 231-K8ikd or 10A-iK8 cells were grown under uninduced (U) or induced (I) conditions for 24 h and RNA was prepared for qRT-PCR and RT-PCR (inset). GAPDH was used as an internal control. B, KLF8 activates MMP14 gene promoter (MMP14p). MCF-10A cells were co-transfected with MMP14p luciferase reporter with wild-type KLF8, its activation domain-defective mutant (mKLF8) or control vector. After 16 hr, luciferase activity was measured. C, KLF8 knockdown reduces MMP14 promoter activity in MDA-MB-231 cells. The MDA-MB-231 cells were transfected with control siRNA or KLF8 siRNA for 48 hrs. The MMP14p reporter was then transfected for reporter assays. MCF-10A cells transfected with the MMP14p was included as a normalizing control. D-F, MMP14 mediates KLF8-induced invasiveness. The 231-K8ikd cells were grown for 24 hours under uninduced conditions (U), induced conditions (I), induced conditions followed by uninduced conditions for 4 days (I → U) or induced conditions plus ectopic expression of MMP14 (I + MMP14). The cells were then used for Matrigel invasion assays (see Materials and Methods) (D). **P < 0.01 and *P < 0.05 compared to lane 2. Effective KLF8 knockdown and recovery (E) and MMP14 overexpression (F) were confirmed by Western blotting. Data represent the mean ± S.D. of at least three independent experiments.