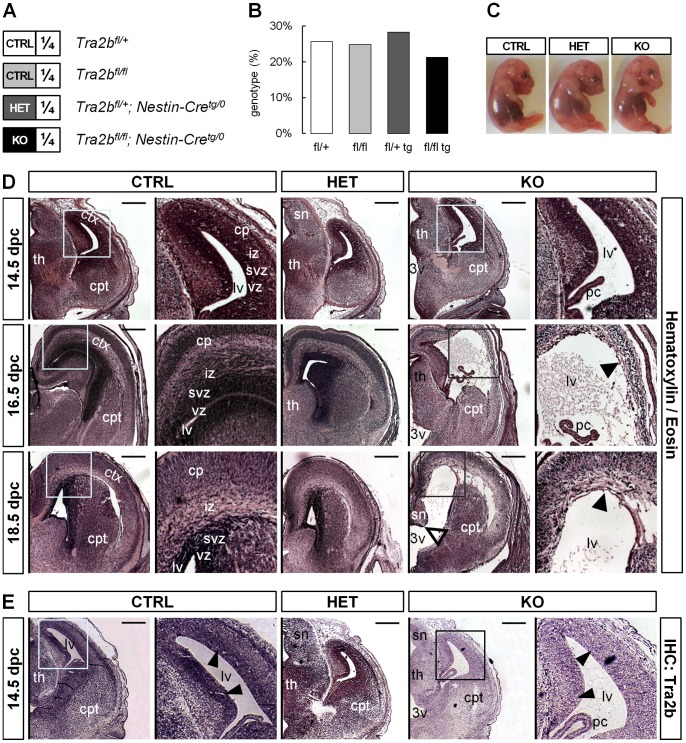
Figure 1. Conditional ablation of Tra2b causes perinatal lethality and disturbed cortical patterning in mice.
(A) Cross breading of Tra2bfl/fl with Tra2bfl/+; Nestin-Cretg/0 mice allowed generation of neuronal-specific knock-out (KO) animals as well as controls (CRTL) and heterozygous knock-out animals (HET) in one litter. (B) KO animals are born alive and all possible genotypes were detected according to Mendelian law (N = 113). (C) General development of conditional knock-out mice is not impaired as there are no gross morphological differences in embryo appearance. (D) Hematoxylin/Eosin staining of paraffin-embedded coronal sections at indicated developmental stages. KO animals but not controls or HET animals show ventriculomegaly of the third and lateral ventricles starting at around 14.5 dpc. Cortical layers are largely distinguishable at 14.5 dpc but cortical patterning and the ependymal lining of the lateral ventricle appears highly disturbed (black arrowheads) at 16.5 dpc in knock-out brains. (E) Immunostaining of Tra2b on paraffin-embedded coronal sections shows efficient downregulation of Tra2b protein in knock-out brains compared to controls and heterozygote animals. Cells of the ventricular and subventricular zones of the cortex show strongest decrease in staining intensity (black arrowhead). Scale bar equals 400 µm; ctx, cortex; th, thalamus; cpt, caudoputamen; cp, cortical plate; iz, intermediate zone; svz, subventricular zone; vz, ventricular zone; sn, septal nuclei; 3v, third ventricle; lv, lateral ventricle; pc, choroid plexus.