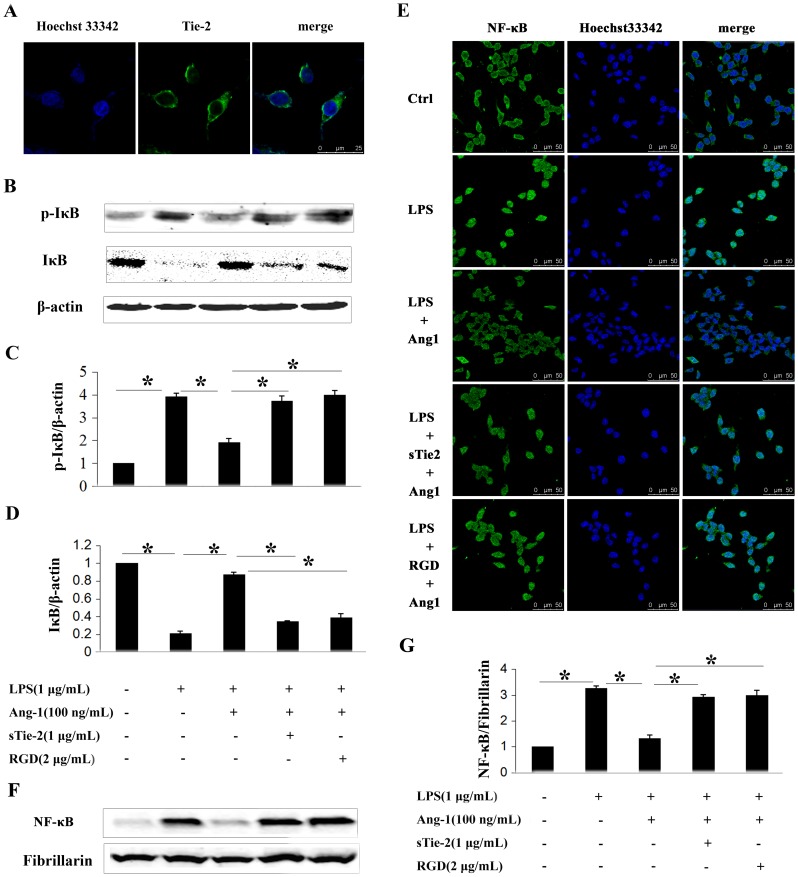
Figure 2. Ang-1 inhibited LPS-induced IκB phosphorylation and NF-κB nuclear translocation in P815 mast cells.
A: Immunofluorescence showed Tie-2 receptor expression. Primary antibody in negative control was monoclonal IgG. B: Western blotting was performed to analyze phosphorylation levels of IκB in mast cells in response to different stimuli. C and D: Densitometric analysis was used to calculate the relative ratio of p-IκB/β-actin (C) and IκB/β-actin (D). Ratio of the control group was arbitrarily presented as 1. *P<0.05. E: NF-κB translocation was detected by confocal microscopy. In quiescent P815 mast cells, NF-κB exerts primarily in the cytoplasm (first panel). With LPS treatment for 2 h, NF-κB translocates into the nucleus (second panel). Ang-1 nearly abolished LPS induced translocation of NF-κB (third panel) which was reversed by soluble form of Tie2 (sTie-2) (forth panel) and RGD (fifth panel). F: NF-κB translocation was also detected by Western blot. Fibrillarin was used as internal control. G: Densitometric analysis was used to calculate the relative ratio of NF-κB/Fibrillarin. Ratio of the control group was arbitrarily presented as 1. Data are mean ± SD of the ratios from 3 independent experiments. *P<0.05.