Figure 7.
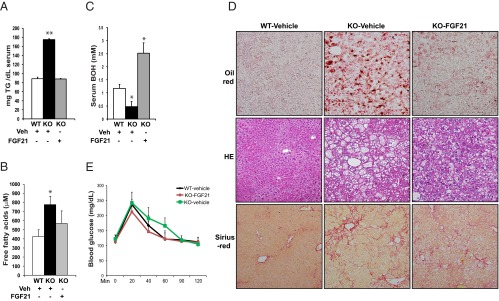
Infusion of recombinant FGF21 protein reverses hypertriglyceridemia, hypoketonemia, and hepatic steatosis, and partially rescues NASH phenotype in CREBH-null mice after the AHF diet. CREBH-null and wild-type (WT) control mice were fed with AHF diet for 6 months before they were injected ip with purified rh FGF21protein (0.1 μg per gram body weight) or vehicle once a day for 8 days. On the sixth day of injection, mice were subjected to fasting blood sample collection and glucose tolerance test after 12-hour fasting. Mice were allowed to recover for 2 days with ongoing injections before they were euthanized and tissues were harvested. A–C, Levels of serum TG, ketone body BOH, and FA in the WT and CREBH-null mice administrated with recombinant FGF21 protein or vehicle (Veh). The blood samples were collected from the mice after 12-hour fasting on the sixth day of administration of FGF21 protein or vehicle. Each bar denotes the mean ± SEM (n = 5 WT or KO mice treated with vehicle and 4 KO mice treated with FGF21). *, P < .05; **, P < .01. D, Histologic staining analysis of liver tissue sections from the wild-type and CREBH-null mice after 8 days of FGF21 protein or vehicle treatment. The upper panel shows the oil-red O staining of hepatic lipid droplets; the middle panel shows hematoxylin and eosin (HE) staining of liver tissue sections; and the lower panel shows Sirius red staining of hepatic collagens. Magnification: ×200. E, Glucose tolerance tests of the CREBH-null and wild-type control mice after 6 days of administration of the FGF21 protein or vehicle. Animals were fasted for 12 hours before being infused with 1 mg d-glucose per gram body weight. Each bar denotes the mean ± SEM (n = 5 WT or KO mice treated with vehicle and 4 KO mice treated with FGF21). KO, CREBH knockout.
