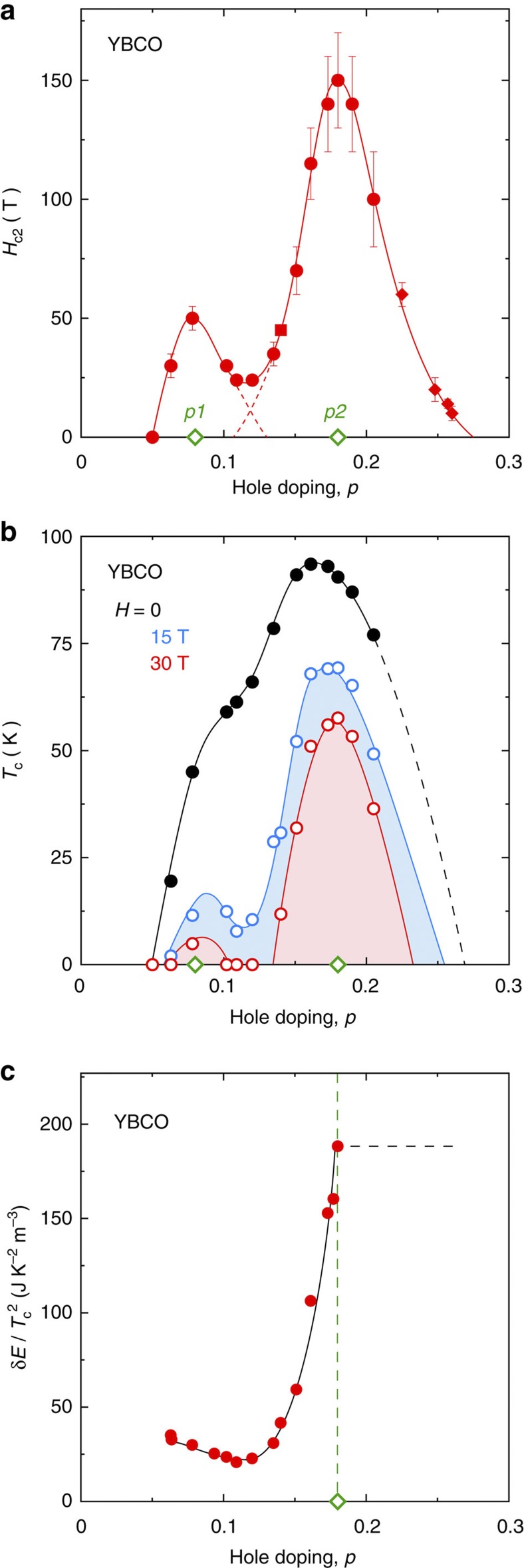
Figure 4. Doping dependence of Hc2, Tc and the condensation energy.
(a) Upper critical field Hc2 of the cuprate superconductor YBCO as a function of hole concentration (doping) p. Hc2 is defined as Hvs(T→0) (Table 1), the onset of the vortex-solid phase at T→0, where Hvs(T) is obtained from high-field resistivity data (Fig. 3, and Supplementary Figs 5 and 6). The point at p=0.14 (square) is from data on Y124 (Fig. 3b). The points at p>0.22 (diamonds) are from data on Tl-2201 (Table 1, Fig. 2 and Supplementary Fig. 6). Error bars on the Hc2 data represent the uncertainty in extrapolating the Hvs(T) data to T=0. (b) Critical temperature Tc of YBCO as a function of doping p, for three values of the magnetic field H, as indicated (Table 1). Tc is defined as the point of zero resistance. All lines are a guide to the eye. Two peaks are observed in Hc2(p) and in Tc(p; H>0), located at p1~0.08 and p2~0.18 (open diamonds). The first peak coincides with the onset of incommensurate spin modulations at p≈0.08, detected by neutron scattering30 and muon spin spectroscopy31. The second peak coincides with the approximate onset of Fermi-surface reconstruction18,21, attributed to charge modulations detected by high-field NMR (ref. 22) and X-ray scattering23,24,25. (c) Condensation energy δE (red circles), given by the product of Hc2 and Hc1 (see Supplementary Note 5 and Supplementary Fig. 8), plotted as δE/Tc2 vs p. Note the eightfold drop below p2 (vertical dashed line), attributed predominantly to a corresponding drop in the density of states. All lines are a guide to the eye.