Figure 4.
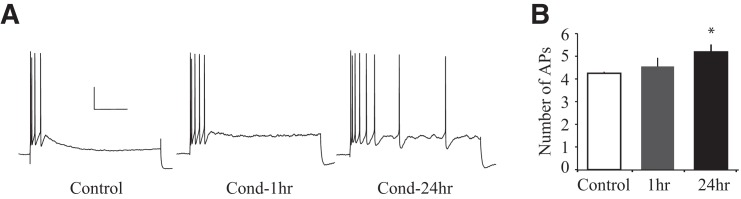
Long-delay fear conditioning reduces spike-frequency adaptation in a time-dependent manner. (A) Representative traces illustrating spike-frequency adaptation in response to a prolonged current injection. Note that LA pyramidal neurons from Control rats (n = 28) but not Cond-24hr rats (n = 28) display remarkable spike-frequency adaptation. Scale: 20 mV, 0.2 sec. (B) Average number of action potentials (APs) during prolonged current injection. LA pyramidal neurons from Cond-24hr rats fire significantly more APs than those from Control rats. Neurons from Cond-1hr rats (n = 13) are not significantly different from any other group. (*) P < 0.05 relative to LA neurons from Control rats.
