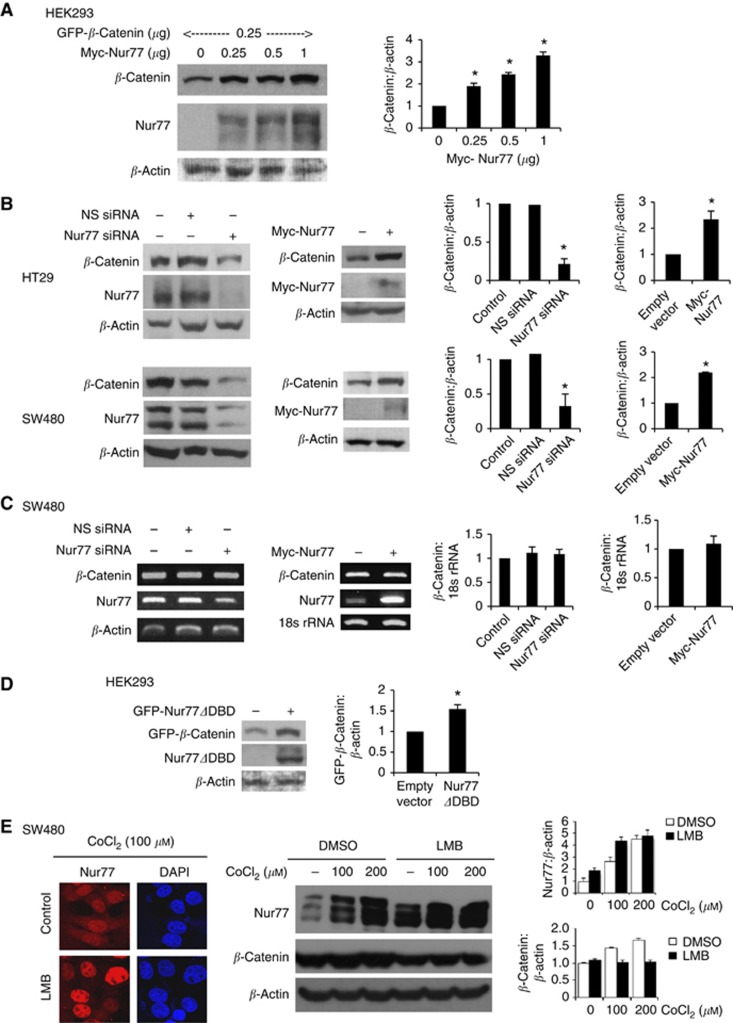
Figure 3.
Hypoxia increases β-catenin protein expression by Nur77 independent of DNA binding. (A) HEK293 cells were transfected with β-catenin expression vector (0.25 μg) and the indicated amount of Nur77 expression vector for 24 h. Transfected cells were then incubated at 1% O2 for 4 h. The total amount of plasmid DNA in all transfections was kept constant using appropriate parental empty expression vectors. Levels of overexpressed Nur77 and β-catenin were analysed by western blotting, with β-actin as a loading control. (B) HT29 and SW480 cells were transfected with non-specific (NS) siRNA or Nur77 siRNA or empty vector and Myc-Nur77. After transfection, cells were exposed to 1% O2 for 4 h, followed by western blotting to detect endogenous β-catenin and Nur77, with β-actin as a loading control. (C) SW480 cells were transfected with NS siRNA or Nur77 siRNA or empty vector or Myc-Nur77. After 24 h of transfection, cells were exposed to 1% O2 for 4 h, followed by RT-PCR to detect mRNA levels of β-catenin and Nur77. 18s rRNA was included as an internal control. (D) HEK293 cells were transfected with Nur77 lacking DNA-binding domain (Nur77ΔDBD) as indicated for 24 h. Cells were then incubated at 1% O2 for 4 h after transfection for 24 h, followed by western blotting. (E) SW480 cells were pretreated with leptomycin B (LMB; 2.5 nM) for 1 h and then exposed to different concentrations of CoCl2 for 4 h. The effect of CoCl2 on Nur77 expression and translocation was analysed by immunostaining using anti-Nur77 antibody (1 : 200). Cells were co-stained with DAPI to visualise the nucleus. β-catenin and Nur77 expression was detected by western blotting. β-Actin expression was served as a loading control. All the immunoblots were quantified by densitometry and the values were normalised with β-actin. The blots shown are representative of three independent experiments. Bar, ±s.d. *P<0.05.