Figure 1. Nonlinear Relationship between Smoking Intensity (Average Number of Cigarettes Smoked per Day) and Lung-Cancer Risk.
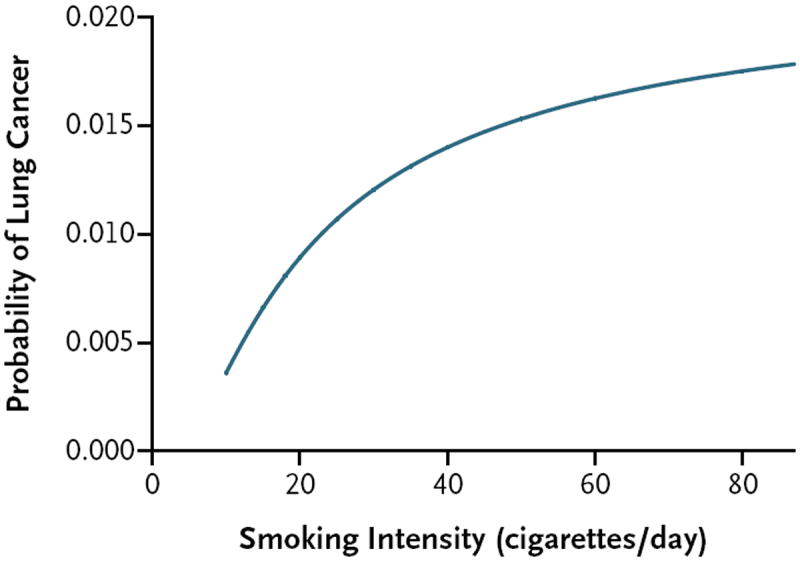
Probabilities were calculated on the basis of the following variables: an age of 62 years, white race or ethnic group, some college education, a body-mass index (the weight in kilograms divided by the square of the height in meters) of 27, no chronic obstructive pulmonary disease, no personal history of cancer, no family history of lung cancer, status as a former smoker, smoking history of 27 years, and cessation of smoking 10 years before enrollment.
