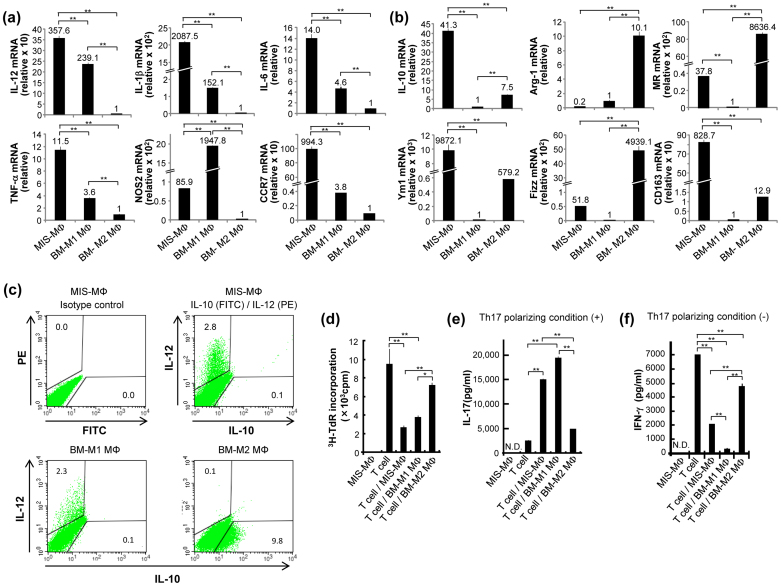
Figure 5. Profiles of mRNA expression of M1 MΦ- and M2 MΦ-specific marker genes by MIS-MΦs.
(a), (b) Total RNAs extracted using ISOGEN kit (Nippon Gene) from MIS-MΦs, BMDM-derived M1-type MΦs (BM-M1 MΦs), and M2-type MΦs (BM-M2 MΦs) were subjected to real-time quantitative RT-PCR for M1 MΦ-marker genes (IL-12, IL-1β, IL-6, TNF-α, NOS2, and CCR7) (a) or M2 MΦ-marker genes (IL-10, Arg-1, MR, Ym1, Fizz, and CD163 (b) as described in Experimental Procedures. (c) MIS-MΦs, BM-M1 MΦs, and BM-M2 MΦs were measured for intercellular expression of IL-12 and IL-10 by cytofluorometry, as described in Fig. 2. Control: MIS-MΦs were stained with FITC-labeled, and PE-labeled rat IgG2b isotype control antibodies. (d–f) Test MΦs were measured for their suppressor activity against T cell mitogenesis (d) and effects on T cell production of IL-17 (e) and IFN-γ (f) as described in Fig. 3. Data are representative of multiple experiments; error bars, s.e.m.; **p < 0.01, *p < 0.05 (Bonferroni's multiple t-test).