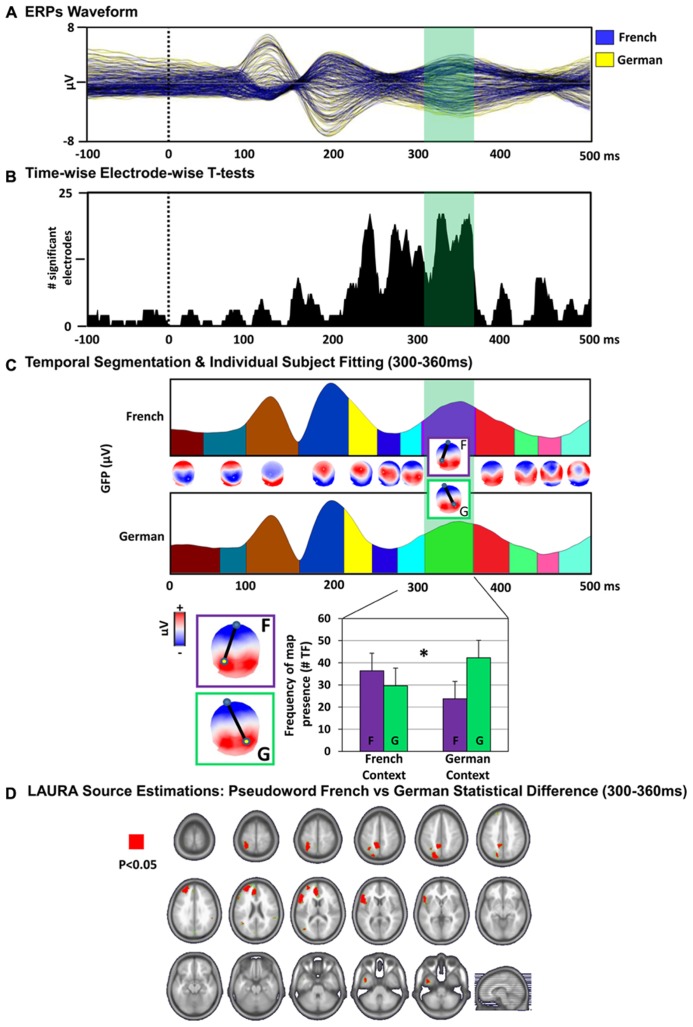
FIGURE 3.
Electrical neuroimaging results. (A) ERPs waveform. The group-averaged ERPs to PW reading in the French (blue) and German (yellow) language context are displayed in microvolts as a function of time relative to stimulus onset (dotted black line). The time period showing significant (p < 0.05) topographic differences between the conditions is indicated in green. (B) Time-wise electrode-wise t-tests. Results of the time-wise paired t-tests at each of the 128 scalp electrodes from the group-averaged ERP waveforms are shown (p < 0.05). (C) Topographic pattern analysis. Top: Topographic pattern analyses identified 12 time periods of stable electric field topography across the collective 500 ms post-stimulus period form the group-averaged ERPs. Topographies (i.e., maps) are shown with the nasion upward and left scalp leftward. The dipole represents the positive and negative maximum of the electric field topography measured at the scalp. Two distinct maps were identified for one of these time periods (300–360 ms) for PWs in the French context (map “F”) versus German context (map “G”) conditions. Bottom: The reliability of this observation at the group-averaged level was assessed at the single-subject level using a spatial correlation fitting procedure. The relative map presence in time frames (TF) of each template map provides a measure for the amount of time a given template map, which was identified in the group-averaged data, is present in an individual subject and condition (see “Material and Methods”). Over the 300–360 ms post-stimulus period, the map “F” characterized more frequently the response to the PWs in the French context and the map “G” in the German context condition. There was a significant interaction between language context condition and map presence over the 300–360 ms period [F(1,13) = 5.91, p = 0.03]. Error bars indicate SEM. (D) Distributed LAURA source estimations. Paired t-tests were performed for each of the 3005 solution points for time-averaged ERPs over the period of topographic modulation (300–360 ms after stimulus onset), revealing differential (p < 0.05) activation of the left inferior frontal gyrus (German > French), left superior parietal gyrus (French > German) and left anterior cinguar cortex (German > French) when reading the PWs in the French versus the German language context.