Fig 2.
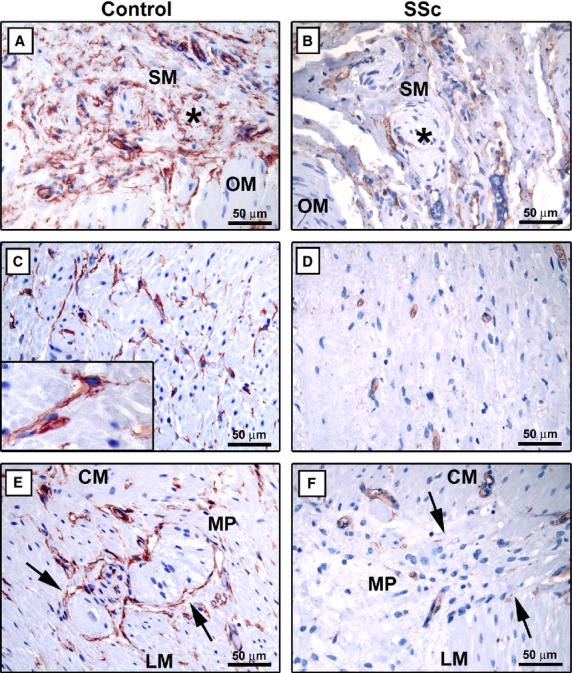
Gastric wall specimens from controls (A, C and E) and patients with systemic sclerosis (SSc) (B, D and F). (A–F) CD34 immunoperoxidase labelling with haematoxylin counterstain. (A and B) Submucosa. (A) In control gastric wall submucosa, telocytes form a network surrounding vessels and ganglia (asterisk) and encircle the submucosal border of the muscularis propria. (B) In the submucosa of SSc gastric wall, very few telocytes entrapped in the fibrotic extracellular matrix are observed. Note the absence of telocytes around submucosal ganglia (asterisk). (C and D) Muscle layers. (C) In the muscularis propria of control gastric wall, numerous telocytes surround smooth muscle bundles and cells. Inset: At higher magnification view, telocytes display a slender nucleated body and very long varicose processes located in the interstitium between smooth muscle cells. (D) Telocytes are very few or absent in muscle layers of SSc gastric wall. (E and F) Myenteric plexus. (E) In control specimens, telocytes form a network enveloping myenteric plexus ganglia (arrows) and are present along the nerve strands of the interganglionic region. (F) Note the almost complete absence of telocytes around myenteric plexus ganglia (arrows) of SSc gastric wall. SM: submucosa; OM: oblique muscle layer; CM: circular muscle layer; LM: longitudinal muscle layer; MP: myenteric plexus. Scale bars are indicated in each panel.
