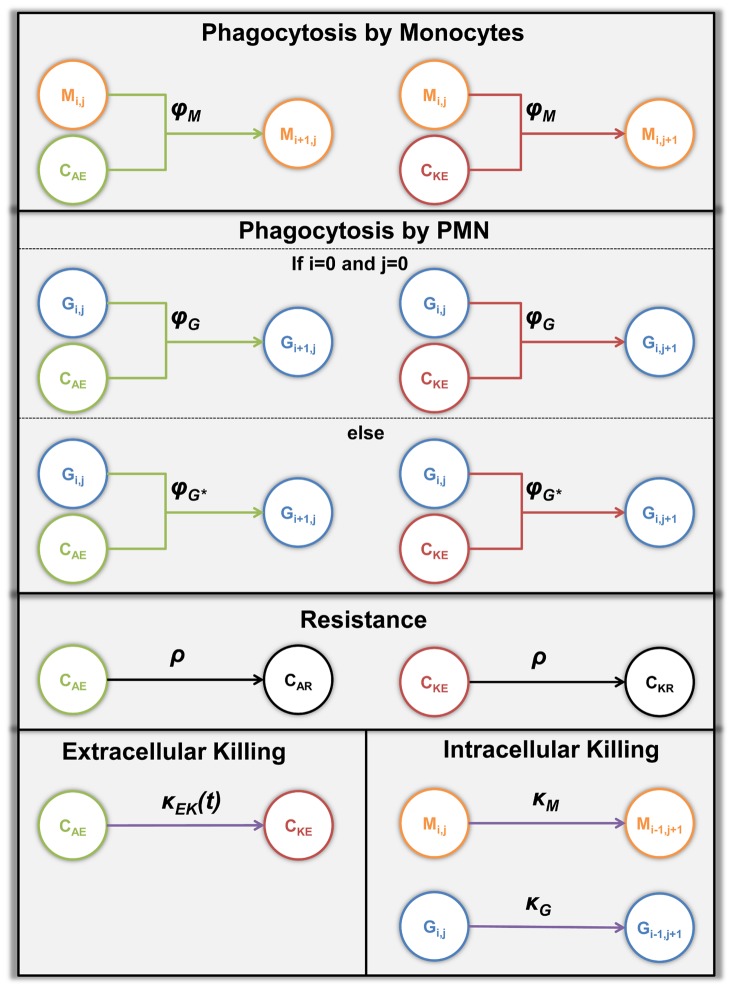
Figure 4. Types of transition in the state-based model.
Illustration of all types of transitions, arranged according to their effect on C. albicans. Circular symbols depict different states and arrows represent transitions between states. Each transition type is associated with a specific transition rate. Extracellular alive C. albicans can be extracellularly killed by antimicrobial effector molecules, i.e. transition from state 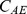 to
to 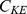 , with rate
, with rate 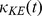 . Alive as well as killed C. albicans can become resistant C. albicans, i.e. transition from state
. Alive as well as killed C. albicans can become resistant C. albicans, i.e. transition from state 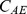 to state
to state 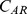 and transition from state
and transition from state 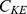 to state
to state 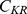 , with transition rate
, with transition rate 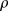 . Furthermore, alive and dead extracellular C. albicans can be phagocytosed by monocytes with rate
. Furthermore, alive and dead extracellular C. albicans can be phagocytosed by monocytes with rate 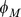 and by PMN that phagocytose for the first time or at least for the second time with rate
and by PMN that phagocytose for the first time or at least for the second time with rate 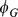 and
and 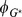 , respectively. Alive C. albicans that were already phagocytosed can be killed intracellular in monocytes with transition rate
, respectively. Alive C. albicans that were already phagocytosed can be killed intracellular in monocytes with transition rate 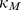 as well in PMN with rate
as well in PMN with rate 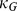 . The monocytes and PMN containing
. The monocytes and PMN containing  alive and
alive and 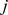 killed C. albicans are represented by
killed C. albicans are represented by 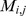 and
and 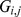 , respectively.
, respectively.