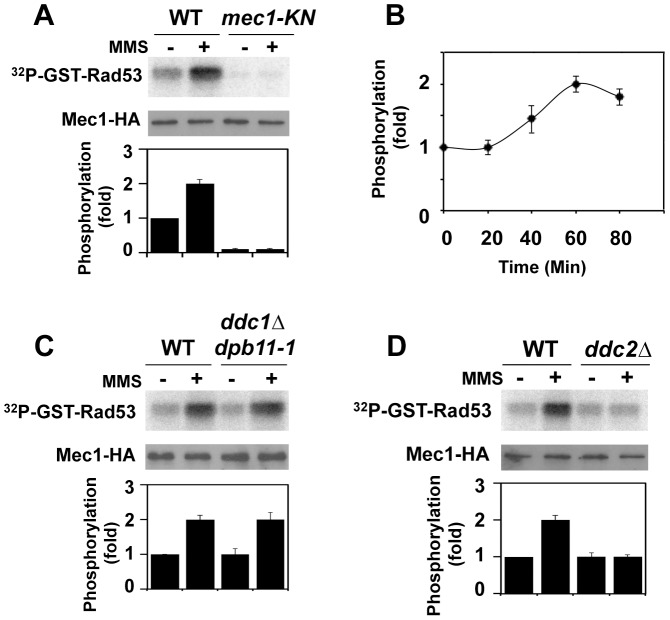
Figure 1. Regulation of protein kinase Mec1 after DNA damage.
(A) Mec1 activation after MMS treatment. Cells expressing Mec1-HA (KSC1635) or Mec1-KN-HA (KSC1645) were cultured at 25°C and incubated with nocodazole to arrest at G2/M. Cells were then either mock treated (−) or treated (+) with 0.05% MMS for 1 hr. Immunoprecipitated Mec1-HA was subjected to the in vitro kinase assay using GST-Rad53, a recombinant protein purified from E. coli, as a substrate. Incorporation of 32P into GST-Rad53 was monitored by phosphorimager. The amounts of Mec1 or Mec1-KN in the immunoprecipitates were determined by immunoblotting with anti-HA antibody. Phosphorylation of GST-Rad53 was normalized to that observed with immunoprecipitated mock treated wild-type Mec1. Relative phosphorylation is determined from three independent experiments. (B) Mec1 activation kinase after incubation with MMS for various lengths of time. Cells were treated with MMS for indicated lengths of time and were subjected to the in vitro kinase assay as in A. (C) Effect of ddc1Δ dpb11-1 mutation on Mec1 activation. Wild-type (KSC1333) and ddc1Δ dpb11-1 (KSC3130) cells expressing Mec1-HA protein were subjected to the in vitro kinase assay as in A. (D) Effect of ddc2Δ mutation on Mec1 activation. Wild-type (KSC1635) and ddc2Δ (KSC1636) cells expressing HA-Mec1 protein were subjected to the in vitro kinase assay as in A.